4、Netty心跳检测机制
所谓心跳,即在TCP长连接中,客户端和服务器之间定期发送的一种特殊的数据包,通知对方自己还在线,以确保TCP连接的有效性。
在Netty中,实现心跳机制的关键是IdleStateHandler类,看下它的构造器:
public IdleStateHandler(int readerIdleTimeSeconds, int writerIdleTimeSeconds, int allIdleTimeSeconds) {
this((long)readerIdleTimeSeconds, (long)writerIdleTimeSeconds, (long)allIdleTimeSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}三个参数的含义:
readerIdleTimeSeconds: 读超时. 即当在指定的时间间隔内没有从Channel读取到数据时, 会触发一个READER_IDLE的 IdleStateEvent事件。
writerIdleTimeSeconds: 写超时. 即当在指定的时间间隔内没有数据写入到Channel时, 会触发一个 WRITER_IDLE的 IdleStateEvent 事件。
allIdleTimeSeconds: 读/写超时。即当在指定的时间间隔内没有读或写操作时, 会触发一个ALL_IDLE的IdleStateEvent事件。
注:这三个参数默认的时间单位是秒。若需要指定其他时间单位,可以使用另一个构造方法:
IdleStateHandler(boolean observeOutput, long readerIdleTime, long writerIdleTime, long allIdleTime, TimeUnit unit)
要实现Netty服务端心跳检测机制需要在服务器端的ChannelInitializer中加入如下的代码:
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(3, 0, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
Netty心跳检测代码示例:
服务端代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(boss, worker)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
//IdleStateHandler的readerIdleTime参数指定超过3秒还没收到客户端的连接,
//会触发IdleStateEvent事件并且交给下一个handler处理,下一个handler必须
//实现userEventTriggered方法处理对应事件
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(3, 0, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
pipeline.addLast(new HeartBeatServerHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("netty server start。。");
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
boss.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
// HeartBeatServerHandler
public class HeartBeatServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
int readIdleTimes = 0;
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务端收到的消息:" + s);
if ("test".equals(s)) {
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("ok");
} else {
System.out.println("其他信息处理...");
}
}
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
String eventType = null;
switch (event.state()) {
case READER_IDLE:
eventType = "读空闲";
readIdleTimes++; // 读空闲的计数加1
break;
case WRITER_IDLE:
eventType = "写空闲";
// 不处理
break;
case ALL_IDLE:
eventType = "读写空闲";
// 不处理
break;
}
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + ":超时事件:" + eventType);
if (readIdleTimes > 3) {
System.out.println(" [server]读空闲超过3次,关闭连接,释放更多资源");
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("close");
ctx.channel().close();
}
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.err.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + " 已上线!");
}
}客户端
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(new HeartBeatClientHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("netty client start。。");
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync().channel();
String text = "test";
Random random = new Random();
while (channel.isActive()) {
int num = random.nextInt(10);
Thread.sleep(num * 1000);
channel.writeAndFlush(text);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
//HeartBeatClientHandler
public class HeartBeatClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
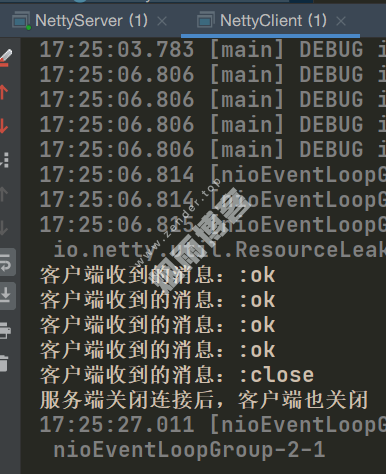
System.out.println("客户端收到的消息::" + msg);
if (msg != null && msg.equals("close")) {
System.out.println("服务端关闭连接后,客户端也关闭");
ctx.channel().closeFuture();
}
}
}Netty断线自动重连实现
/**
* 实现了重连的客户端
*/
public class NettyClient {
private String host;
private int port;
private Bootstrap bootstrap;
private EventLoopGroup group;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
NettyClient nettyClient = new NettyClient("localhost", 9000);
nettyClient.connect();
}
public NettyClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
init();
}
private void init() {
//客户端需要一个事件循环组
group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//创建客户端启动对象
// bootstrap 可重用, 只需在NettyClient实例化的时候初始化即可.
bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//加入处理器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyClientHandler(NettyClient.this));
}
});
}
public void connect() throws Exception {
System.out.println("netty client start。。");
//启动客户端去连接服务器端
ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.connect(host, port);
cf.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
//重连交给后端线程执行
future.channel().eventLoop().schedule(() -> {
System.err.println("重连服务端...");
try {
connect();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, 3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
System.out.println("服务端连接成功...");
}
}
});
//对通道关闭进行监听
cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}
}
// NettyClientHandler
public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private NettyClient nettyClient;
public NettyClientHandler(NettyClient nettyClient) {
this.nettyClient = nettyClient;
}
/**
* 当客户端连接服务器完成就会触发该方法
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("HelloServer".getBytes(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf);
}
//当通道有读取事件时会触发,即服务端发送数据给客户端
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("收到服务端的消息:" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("服务端的地址: " + ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
}
// channel 处于不活动状态时调用
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.err.println("运行中断开重连。。。");
nettyClient.connect();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}版权声明
非特殊说明,本文由Zender原创或收集发布,欢迎转载。
上一篇:3、Netty编解码、粘包拆包 下一篇:1、Dubbo基础
 ZENDER
ZENDER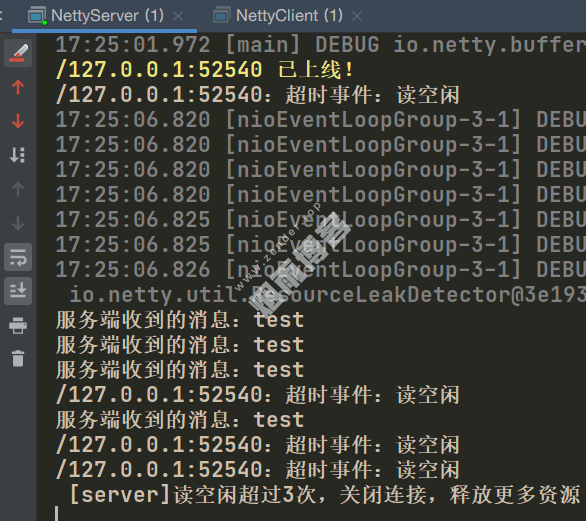
发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。