3、Netty编解码、粘包拆包
一、编码、解码器
当你通过Netty发送或者接受一个消息的时候,就将会发生一次数据转换。
入站消息会被解码:从字节转换为另一种格式(比如java对象);如果是出站消息,它会被编码成字节。
Netty提供了一系列实用的编码解码器,他们都实现了ChannelInboundHadnler(入站)或者ChannelOutboundHandler(出站)接口。在这些类中,channelRead方法已经被重写了。
以入站为例,对于每个从入站Channel读取的消息,这个方法会被调用。随后,它将调用由已知解码器所提供的decode()方法进行解码,并将已经解码的字节转发给ChannelPipeline中的下一个ChannelInboundHandler。Netty提供了很多编解码器,比如编解码字符串的StringEncoder和StringDecoder,编解码对象的ObjectEncoder和ObjectDecoder等。
如果要实现高效的编解码可以用protobuf,但是protobuf需要维护大量的proto文件比较麻烦,现在一般可以使用protostuff。protostuff是一个基于protobuf实现的序列化方法,它较于protobuf最明显的好处是,在几乎不损耗性能的情况下做到了不用我们写.proto文件来实现序列化。使用它也非常简单,代码如下:
<dependency> <groupId>com.dyuproject.protostuff</groupId> <artifactId>protostuff-api</artifactId> <version>1.0.10</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.dyuproject.protostuff</groupId> <artifactId>protostuff-core</artifactId> <version>1.0.10</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.dyuproject.protostuff</groupId> <artifactId>protostuff-runtime</artifactId> <version>1.0.10</version> </dependency>
工具类
/**
* protostuff 序列化工具类,基于protobuf封装
*/
public class ProtostuffUtil {
private static Map<Class<?>, Schema<?>> cachedSchema = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, Schema<?>>();
private static <T> Schema<T> getSchema(Class<T> clazz) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Schema<T> schema = (Schema<T>) cachedSchema.get(clazz);
if (schema == null) {
schema = RuntimeSchema.getSchema(clazz);
if (schema != null) {
cachedSchema.put(clazz, schema);
}
}
return schema;
}
/**
* 序列化
*/
public static <T> byte[] serializer(T obj) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<T> clazz = (Class<T>) obj.getClass();
LinkedBuffer buffer = LinkedBuffer.allocate(LinkedBuffer.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
try {
Schema<T> schema = getSchema(clazz);
return ProtostuffIOUtil.toByteArray(obj, schema, buffer);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
buffer.clear();
}
}
/**
* 反序列化
*/
public static <T> T deserializer(byte[] data, Class<T> clazz) {
try {
T obj = clazz.newInstance();
Schema<T> schema = getSchema(clazz);
ProtostuffIOUtil.mergeFrom(data, obj, schema);
return obj;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}准备一个user对象
public class User implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
public User(){}
public User(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}服务端
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new NettyServerHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("netty server start。。");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
//NettyServerHandler
public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//用protostuff解码
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] bytes = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(bytes);
System.out.println("从客户端读取到Object:" + ProtostuffUtil.deserializer(bytes, User.class));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}客户端
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new NettyClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
//NettyClientHandler
public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("收到服务器消息:" + msg);
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyClientHandler发送数据");
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(ProtostuffUtil.serializer(new User(1, "zender")));
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf);
}
}运行结果
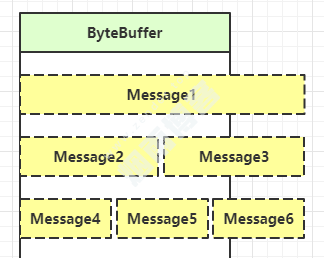
二、粘包拆包
情况1:Message1消息过大,导致半包。
情况2:Message2 Message3消息小,导致半包。
情况2:Message4 Message4 Message6消息小,导致粘包。
2.1、解决方案
消息定长度,传输的数据大小固定长度,例如每段的长度固定为100字节,如果不够空位补空格(很少用)。
在数据包尾部添加特殊分隔符,比如下划线,中划线等,这种方法简单易行,但选择分隔符的时候一定要注意每条数据的内部一定不能出现分隔符。
发送长度:发送每条数据的时候,将数据的长度一并发送,比如可以选择每条数据的前4位是数据的长度,应用层处理时可以根据长度来判断每条数据的开始和结束(常用)。
Netty提供了多个解码器,可以进行分包的操作,如下:
服务端
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//添加自定义解密类
pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageDecoder());
//处理对象类
pipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("netty server start。。");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
// MyServerHandler
public class MyServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MyMessageProtocol> {
private int count;
@Override
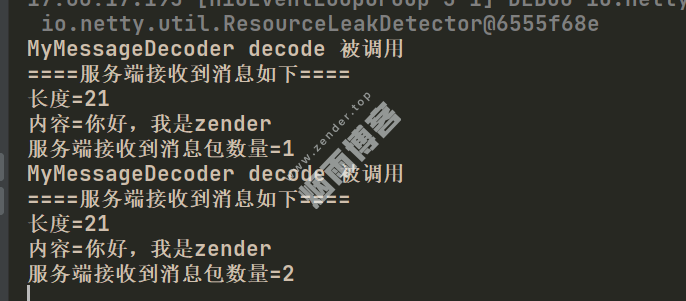
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MyMessageProtocol msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("====服务端接收到消息如下====");
System.out.println("长度=" + msg.getLen());
System.out.println("内容=" + new String(msg.getContent(), CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("服务端接收到消息包数量=" + (++this.count));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
/**
* 自定义协议包
*/
public class MyMessageProtocol {
//定义一次发送包体长度
private int len;
//一次发送包体内容
private byte[] content;
public int getLen() {
return len;
}
public void setLen(int len) {
this.len = len;
}
public byte[] getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(byte[] content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
/**
* 自定义消息加密类
*/
public class MyMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<MyMessageProtocol> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MyMessageProtocol msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
out.writeInt(msg.getLen());
out.writeBytes(msg.getContent());
}
}
/**
* 自定义消息解码类
*/
public class MyMessageDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
int length = 0;
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyMessageDecoder decode 被调用");
//需要将得到二进制字节码-> MyMessageProtocol数据包(对象)
if(in.readableBytes() >= 4) {
if (length == 0){
length = in.readInt();
}
if (in.readableBytes() < length) {
System.out.println("当前可读数据不够,继续等待。。");
return;
}
byte[] content = new byte[length];
if (in.readableBytes() >= length){
in.readBytes(content);
//封装成MyMessageProtocol对象,传递到下一个handler业务处理
//也就是自己定义的MyServerHandler.class
MyMessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MyMessageProtocol();
messageProtocol.setLen(length);
messageProtocol.setContent(content);
out.add(messageProtocol);
}
length = 0;
}
}
}客户端
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(new MyClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
// MyClientHandler
public class MyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MyMessageProtocol> {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
for(int i = 0; i< 2; i++) {
String msg = "你好,我是zender";
//创建协议包对象
MyMessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MyMessageProtocol();
messageProtocol.setLen(msg.getBytes(CharsetUtil.UTF_8).length);
messageProtocol.setContent(msg.getBytes(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
ctx.writeAndFlush(messageProtocol);
}
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MyMessageProtocol msg) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}版权声明
非特殊说明,本文由Zender原创或收集发布,欢迎转载。
上一篇:2、Netty线程模型 下一篇:4、Netty心跳检测机制
 ZENDER
ZENDER
发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。