Spring AOP
一、什么是AOP
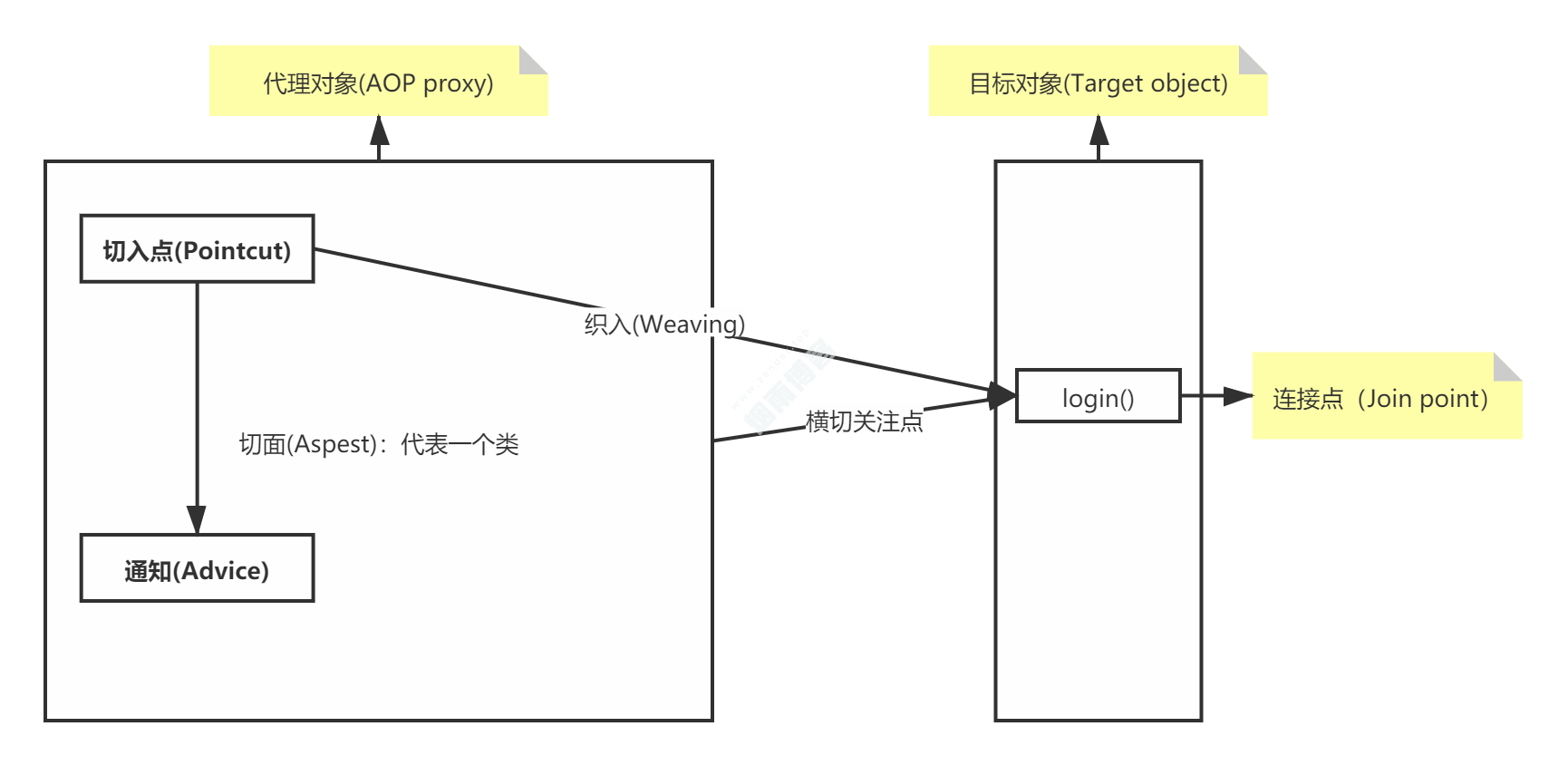
二、AOP重要的术语(概念)
2.1、Spring官网描述的AOP 概念
Aspect: A modularization of a concern that cuts across multiple classes. Transaction management is a good example of a crosscutting concern in enterprise Java applications. In Spring AOP, aspects are implemented by using regular classes (the schema-based approach) or regular classes annotated with the @Aspect annotation (the @AspectJ style).
(翻译)跨越多个 classes 的关注点的模块化。 Transaction management 是企业 Java applications 中横切关注点的一个很好的例子。在 Spring AOP 中,方面是使用常规 classes(schema-based 接近)或使用
@Aspectannotation(@AspectJ 风格)注释的常规 classes 实现的。Join point: A point during the execution of a program, such as the execution of a method or the handling of an exception. In Spring AOP, a join point always represents a method execution.
(翻译)程序执行期间的一个点。例如方法的执行或 exception 的处理。在 Spring AOP 中,连接点始终表示方法的执行。
Advice: Action taken by an aspect at a particular join point. Different types of advice include “around”, “before” and “after” advice. (Advice types are discussed later.) Many AOP frameworks, including Spring, model an advice as an interceptor and maintain a chain of interceptors around the join point.
(翻译)aspect 在特定连接点采取的操作。不同类型的建议包括“周围”,“之前”和“之后”建议。 (建议类型被讨论 later.)许多 AOP 框架,包括 Spring,model 作为拦截器的建议,并在连接点周围维护一系列拦截器。
Pointcut: A predicate that matches join points. Advice is associated with a pointcut expression and runs at any join point matched by the pointcut (for example, the execution of a method with a certain name). The concept of join points as matched by pointcut expressions is central to AOP, and Spring uses the AspectJ pointcut expression language by default.
(翻译)匹配连接点的谓词。建议与切入点表达式相关联,并在切入点匹配的任何连接点处运行(对于 example,执行具有特定 name 的方法)。由切入点表达式匹配的连接点的概念是 AOP 的核心,而 Spring 默认使用 AspectJ 切入点表达式语言。
Introduction: Declaring additional methods or fields on behalf of a type. Spring AOP lets you introduce new interfaces (and a corresponding implementation) to any advised object. For example, you could use an introduction to make a bean implement an IsModified interface, to simplify caching. (An introduction is known as an inter-type declaration in the AspectJ community.)
(翻译)代表类型声明其他方法或字段。 Spring AOP 允许您向任何建议的 object 引入新接口(以及相应的 implementation)。对于 example,您可以使用简介使 bean 实现
IsModified接口,以简化缓存。 (引言在 AspectJ 中被称为 inter-type 声明 community.)Target object: An object being advised by one or more aspects. Also referred to as the “advised object”. Since Spring AOP is implemented by using runtime proxies, this object is always a proxied object.
(翻译)由一个或多个方面建议的 object。也称为“建议对象”。由于 Spring AOP 是使用运行时代理实现的,因此 object 始终是代理 object。
AOP proxy: An object created by the AOP framework in order to implement the aspect contracts (advise method executions and so on). In the Spring Framework, an AOP proxy is a JDK dynamic proxy or a CGLIB proxy.
(翻译)由 order 中的 AOP framework 创建的 object,用于实现 aspect contracts(建议方法执行等)。在 Spring Framework 中,AOP 代理是 JDK 动态代理或 CGLIB 代理。
Weaving: linking aspects with other application types or objects to create an advised object. This can be done at compile time (using the AspectJ compiler, for example), load time, or at runtime. Spring AOP, like other pure Java AOP frameworks, performs weaving at runtime.
(翻译)将方面与其他 application 类型或 objects 链接以创建一个建议的 object。这可以在 compile time(使用 AspectJ 编译器,example),load time 或运行时完成。与其他纯 Java AOP 框架一样,Spring AOP 在运行时执行编织。
2.2、理解
2.3、另一种理解
a. 连接点(Joinpoint):程序执行的某个特定位置(如:某个方法调用前、调用后,方法抛出异常后)。一个类或一段程序代码拥有一些具有边界性质的特定点,这些代码中的特定点就是连接点。Spring仅支持方法的连接点。
b. 切点(Pointcut):如果连接点相当于数据中的记录,那么切点相当于查询条件,一个切点可以匹配多个连接点。Spring AOP的规则解析引擎负责解析切点所设定的查询条件,找到对应的连接点。
c. 增强(Advice):增强是织入到目标类连接点上的一段程序代码。Spring提供的增强接口都是带方位名的,如:BeforeAdvice、AfterReturningAdvice、ThrowsAdvice等。很多资料上将增强译为“通知”,这明显是个词不达意的翻译,让很多程序员困惑了许久。
说明: Advice在国内的很多书面资料中都被翻译成”通知”,但是很显然这个翻译无法表达其本质,有少量的读物上将这个词翻译为”增强”,这个翻译是对Advice较为准确的诠释,我们通过AOP将横切关注功能加到原有的业务逻辑上,这就是对原有业务逻辑的一种增强,这种增强可以是前置增强、后置增强、返回后增强、抛异常时增强和包围型增强。
d. 引介(Introduction):引介是一种特殊的增强,它为类添加一些属性和方法。这样,即使一个业务类原本没有实现某个接口,通过引介功能,可以动态的未该业务类添加接口的实现逻辑,让业务类成为这个接口的实现类。
e. 织入(Weaving):织入是将增强添加到目标类具体连接点上的过程,AOP有三种织入方式:①编译期织入:需要特殊的Java编译期(例如AspectJ的ajc);②装载期织入:要求使用特殊的类加载器,在装载类的时候对类进行增强;③运行时织入:在运行时为目标类生成代理实现增强。Spring采用了动态代理的方式实现了运行时织入,而AspectJ采用了编译期织入和装载期织入的方式。
f. 切面(Aspect):切面是由切点和增强(引介)组成的,它包括了对横切关注功能的定义,也包括了对连接点的定义。
AOP是一种概念。Spring AOP、AspectJ都是AOP的实现,Spring AOP有自己的语法,但是语法复杂,所以Spring AOP借助了AspectJ的注解,但是底层实现还是自己的。
三、使用Spring AOP
Spring AOP includes the following types of advice:
Before advice: Advice that runs before a join point but that does not have the ability to prevent execution flow proceeding to the join point (unless it throws an exception).
After returning advice: Advice to be run after a join point completes normally (for example, if a method returns without throwing an exception).
After throwing advice: Advice to be executed if a method exits by throwing an exception.
After (finally) advice: Advice to be executed regardless of the means by which a join point exits (normal or exceptional return).
Around advice: Advice that surrounds a join point such as a method invocation. This is the most powerful kind of advice. Around advice can perform custom behavior before and after the method invocation. It is also responsible for choosing whether to proceed to the join point or to shortcut the advised method execution by returning its own return value or throwing an exception.
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.0.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.5</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
3.1、使用Java Configuration + 注解方式实现AOP
//表示该类是个配置类
@Configuration
//扫描包
@ComponentScan("com.zender")
//启动AspectJ的支持
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig {
}定义一个Dao,并交给Spring管理:
@Component
public class IndexDao {
public void query(){
System.out.println("query DB!");
}
}声明一个切面,并交给Spring管理:
@Component
//表示该类是一个切面
@Aspect
public class IndexAspect {
/**
* 声明了一个切入点:切入点里面有连接点
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.zender.dao.*.*(..))")
public void pointCut(){}
/**
* 声明一个前置通知:包含通知的位置、通知的内容
*/
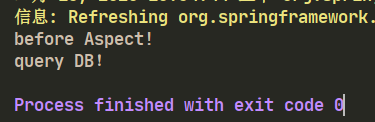
@Before("pointCut()")
public void before(){
//通知的内容
System.out.println("before Aspect!");
}
}测试:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
IndexDao indexDao = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(IndexDao.class);
indexDao.query();
}
}3.2、使用xml方式实现AOP
3.3、实现xxxAdvice接口方式实现AOP
四、Spring支持的AspectJ切入点标志
Supported Pointcut Designators
Spring AOP supports the following AspectJ pointcut designators (PCD) for use in pointcut expressions:
execution: For matching method execution join points. This is the primary pointcut designator to use when working with Spring AOP.within: Limits matching to join points within certain types (the execution of a method declared within a matching type when using Spring AOP).this: Limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the bean reference (Spring AOP proxy) is an instance of the given type.target: Limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the target object (application object being proxied) is an instance of the given type.args: Limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the arguments are instances of the given types.@target: Limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the class of the executing object has an annotation of the given type.@args: Limits matching to join points (the execution of methods when using Spring AOP) where the runtime type of the actual arguments passed have annotations of the given types.@within: Limits matching to join points within types that have the given annotation (the execution of methods declared in types with the given annotation when using Spring AOP).@annotation: Limits matching to join points where the subject of the join point (the method being executed in Spring AOP) has the given annotation.
4.1、execution语法格式
//execution语法格式:execution(<修饰符模式>? <返回类型模式> <方法名模式>(<参数模式>) <异常模式>?)
//标注?的项目表示着可以省略
/*
整个表达式可以分为五个部分:
1、execution(): 表达式主体。
2、第一个*号:表示返回类型,*号表示所有的类型。
3、包名:表示需要拦截的包名,后面的两个句点表示当前包和当前包的所有子包,com.zender.dao包、子孙包下所有类的方法。
4、第二个*号:表示类名,*号表示所有的类。
5、*(..):最后这个星号表示方法名,*号表示所有的方法,后面括弧里面表示方法的参数,两个句点表示任何参数。
*/
@pointcut("execution(* com.zender.dao.*.*(..))")4.2、within
@Pointcut("within(com.zender.dao.*)")
public void pointCutWithin(){
}
//com.zender.dao包及子包下的任何方法执行。
@Pointcut("within(com.zender.dao..*)")
//com.zender.dao包或所有子包下IPointcutService类型及子类型的任何方法。
@Pointcut("within(com.zender.dao..IPointcutService+)")
//持有@org.springframework.stereotype.Component注解的任何类型的任何方法,必须是在目标对象上声明这个注解,在接口上声明的对它不起作用。
@Pointcut("within(@org.springframework.stereotype.Component *)")4.3、this
//当前代理对象实现了 IPointcutService接口的任何方法。
@Pointcut("this(cn.javass.spring.chapter6.service.IPointcutService)")
public void pointCutThis(){
}4.4、target
//当前目标对象(非代理对象)实现了 IPointcutService接口的任何方法。
@Pointcut("target(cn.javass.spring.chapter6.service.IPointcutService)")
public void pointCutTarget(){
}4.5、args
//任何一个以接受“传入参数类型为 java.io.Serializable”开头,且其后可跟任意个任意类型的参数的方法执行,args指定的参数类型是在运行时动态匹配的。
@Pointcut("args(java.io.Serializable,..)")
public void pointCutArgs(){
}4.6、@target
//任何目标对象持有Secure注解的类方法;必须是在目标对象上声明这个注解,在接口上声明的对它不起作用。
@Pointcut("@target(cn.javass.spring.chapter6.Secure)")
public void pointCutTarget(){
}4.7、@args
//任何一个只接受一个参数的方法,且方法运行时传入的参数持有注解 cn.javass.spring.chapter6.Secure;动态切入点,类似于arg指示符。
@Pointcut("@args(cn.javass.spring.chapter6.Secure)")
public void pointCutArgs(){
}4.8、@within
//任何目标对象对应的类型持有Secure注解的类方法;必须是在目标对象上声明这个注解,在接口上声明的对它不起作用。
@Pointcut("@within(cn.javass.spring.chapter6.Secure)")
public void pointCutWithin(){
}4.9、@annotation
//当前执行方法上持有注解 cn.javass.spring.chapter6.Secure将被匹配。
@Pointcut("@annotation(cn.javass.spring.chapter6.Secure)")
public void pointCutAnnotation(){
}版权声明
非特殊说明,本文由Zender原创或收集发布,欢迎转载。
 ZENDER
ZENDER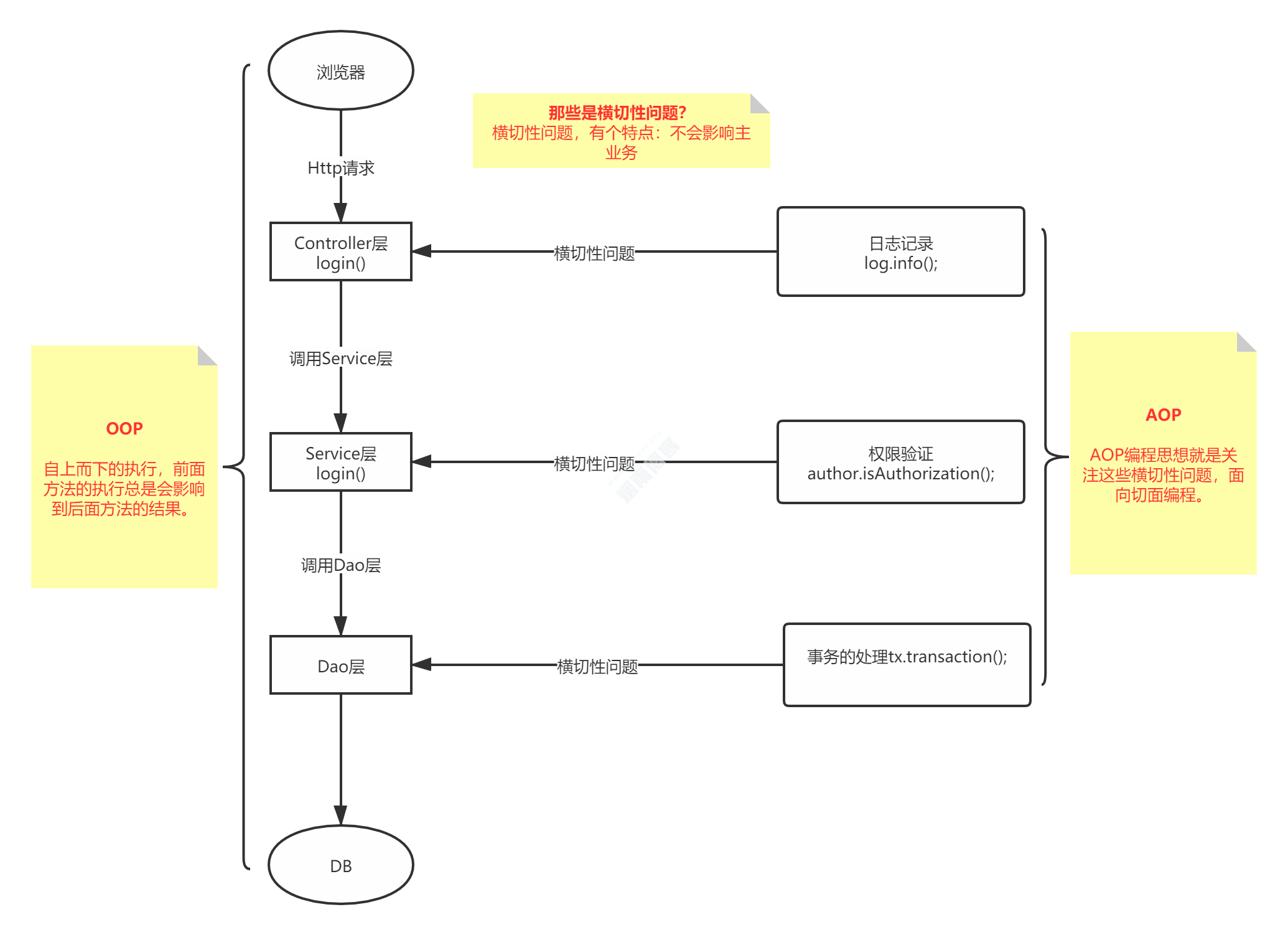



发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。