3、Mybatis源码-Mybatis配置解析
一、入门案例
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String resource = "mybatis.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//从调用者角度来讲,利用SqlSession对象与数据库打交道
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//通过动态代理去帮我们执行SQL
DemoMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DemoMapper.class);
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id","1");
System.out.println(mapper.selectAll(map));
sqlSession.close();
}执行流程如下:
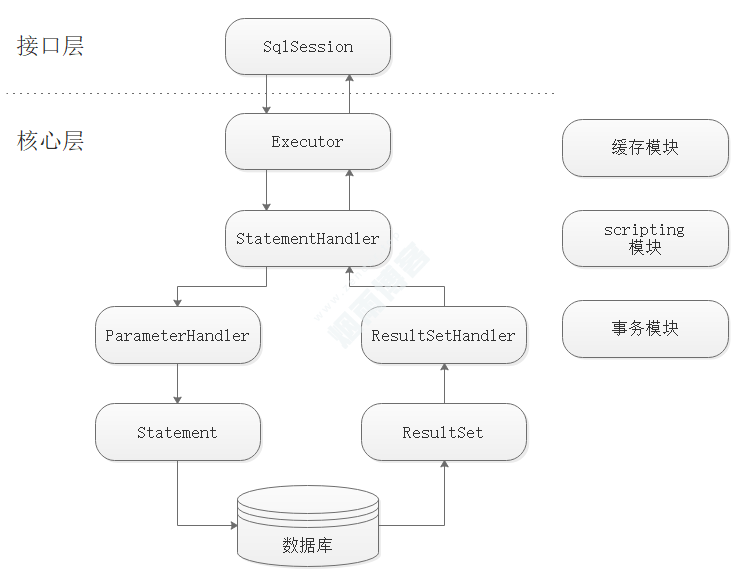
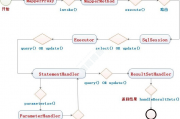
首先通过 Java API 或者 XML 配置完成初始化,最终所有的配置都在 Configuration 类中维护。
然后通过 SqlSessionFactory 得到 SqlSession,这里 SqlSession 就是 mybatis 的顶层 API 了,主要通过他完成数据库的增删改查等操作。
然后 SqlSession 将具体的操作委托给 Executor 执行,Executor 就是 mybatis 的调度核心了,主要职责有 SQL 语句生成、一二级缓存维护和事务的相关操作。
然后 Executor 将数据库相关的操作委托给 StatementHandler,StatementHandler 中完成了 mybatis 最核心的工作,包括参数绑定,指定 SQL 语句,结果集映射等。
1.1、创建会话工厂类时序图
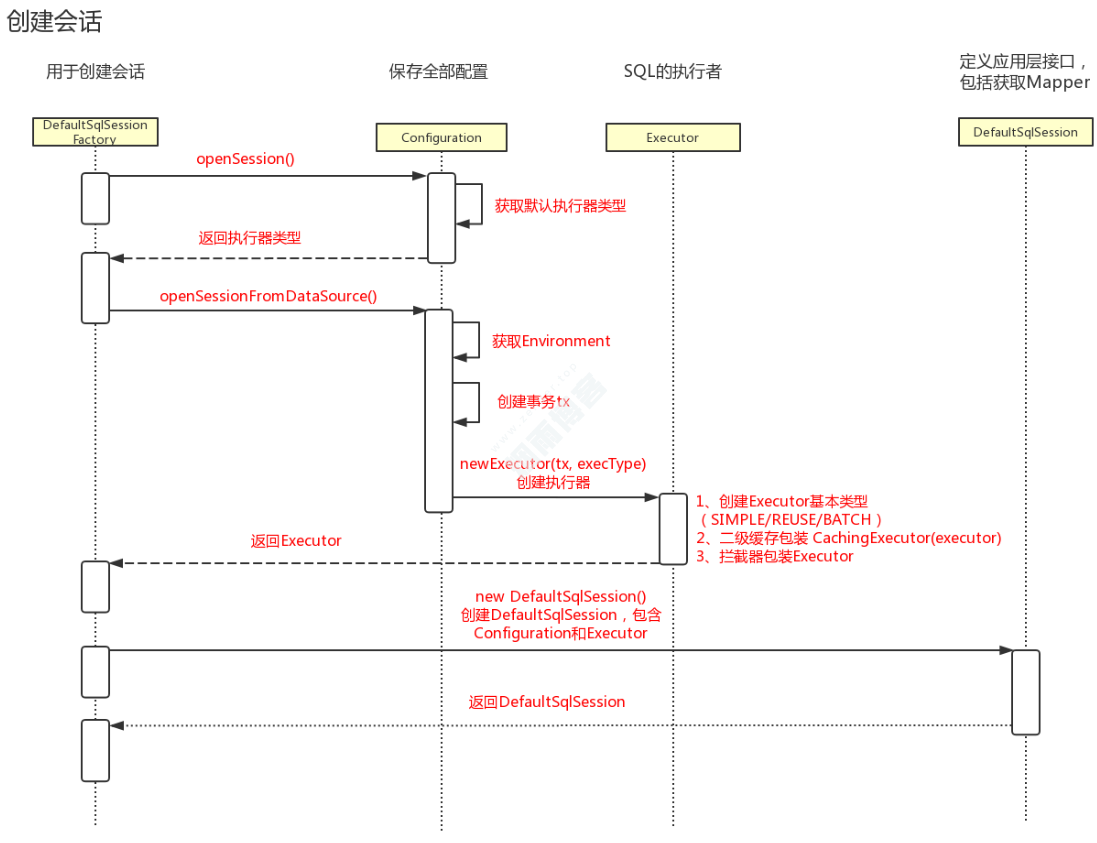
1.2、创建会话时序图
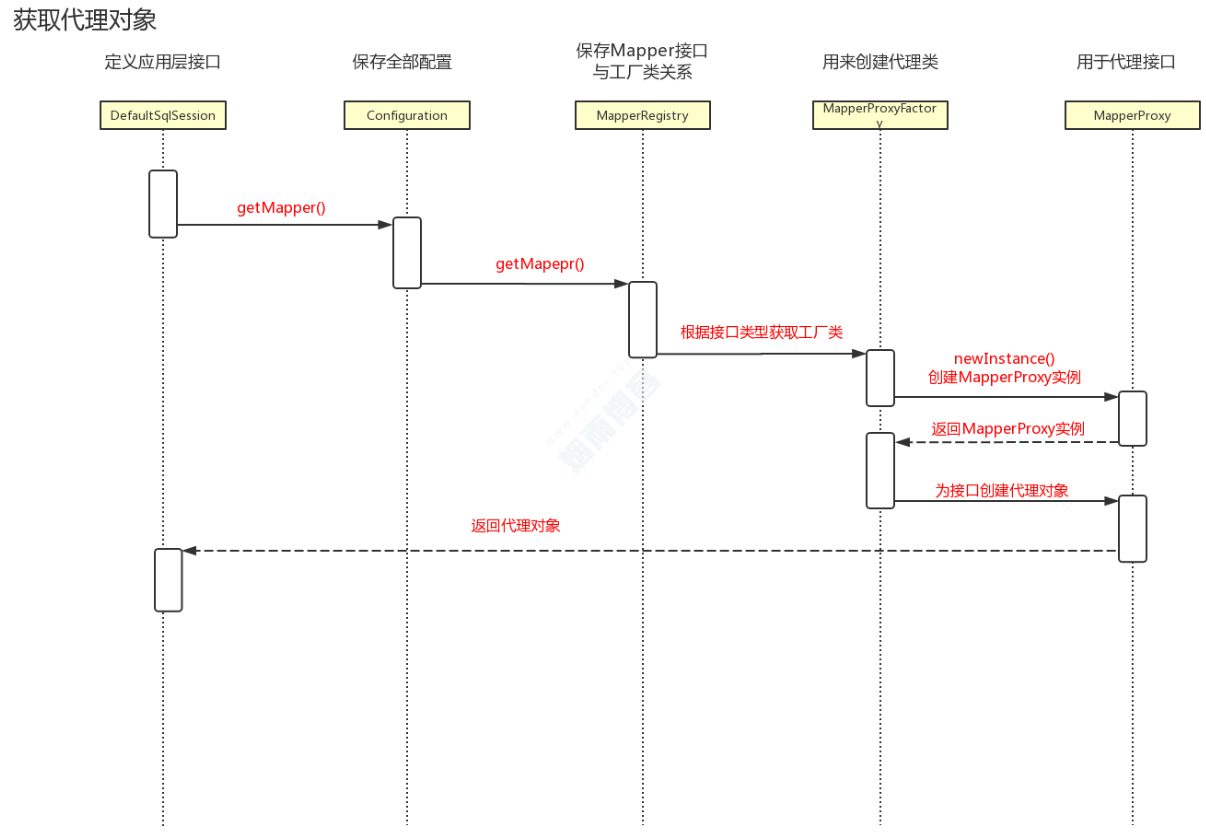
1.3、获取代理类时序图
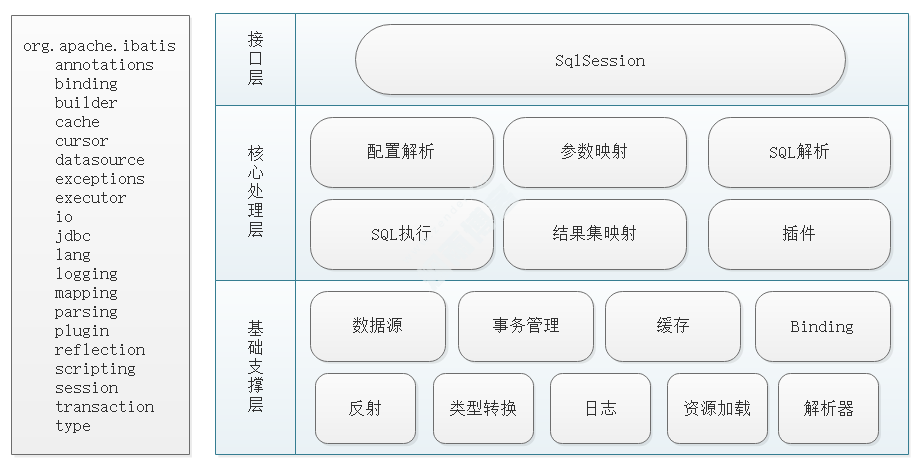
二,mybatis模块结构图
SqlSession:Mybatis核心接口,表示一次数据库的会话。
Executor:它是一个执行器,真正与数据库交互的对象。
StatementHandler:处理sql语句预编译,设置参数等相关工作。
ParameterHandler:设置预编译参数。
ResultHandler:处理结果集,并封装。
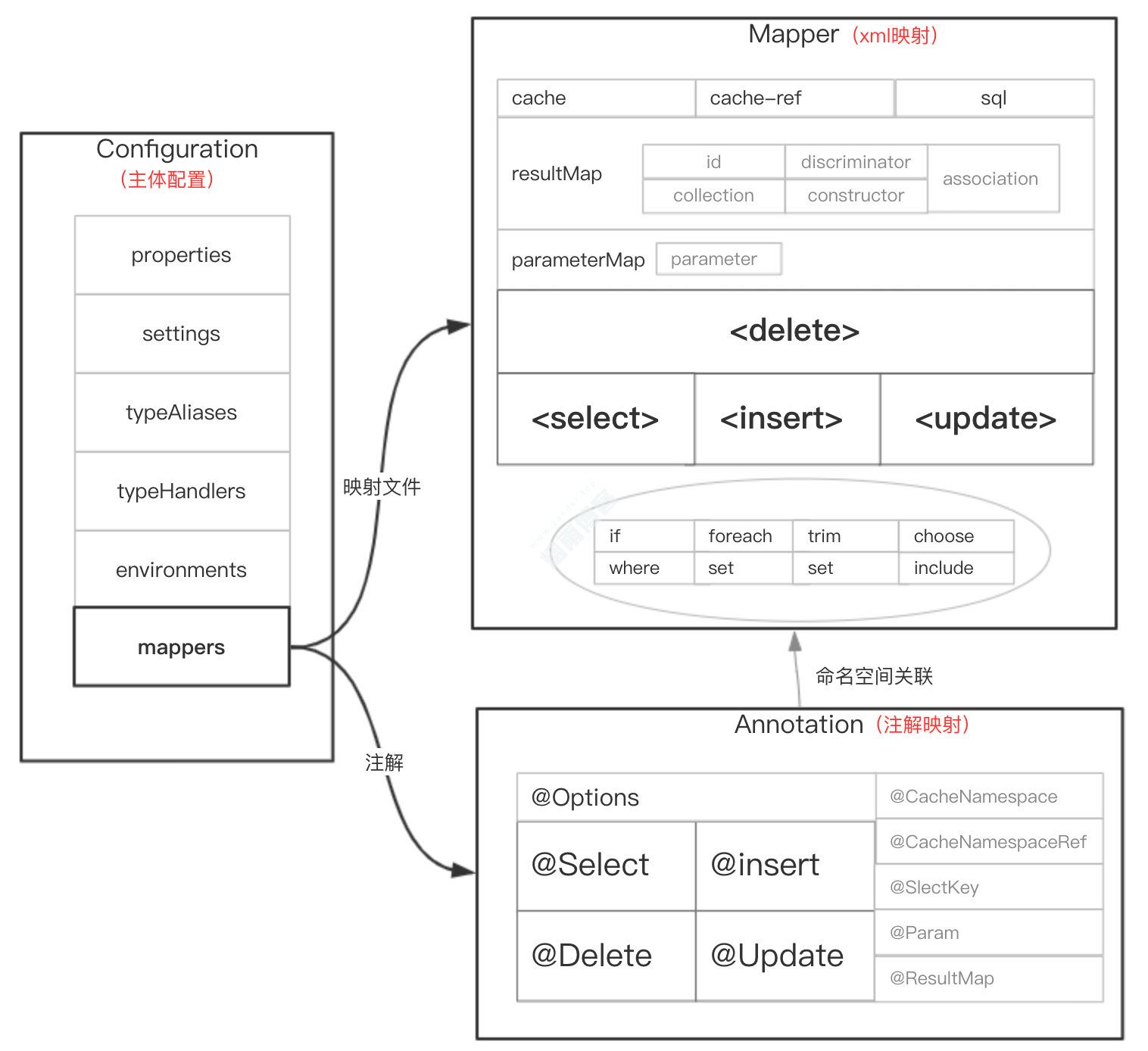
三、MyBatis配置体系
四,核心config.xml具体解析流程
4.1、通过XmlConfigBuilder作为入口
/**
* @param inputStream
* @param environment 环境id,等同标签<environment id="development"></environment>
* @param properties 额外的配置
* @return
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
//解析config.xml(mybatis解析xml是用的java dom)
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
//parser.parse(): 解析config.xml里面的节点,构成一个Configuration对象。
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}XML初始化的主要流程被封装到了XMLConfigBuilder 当中,逻辑如下:
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//第1步:解析xml文件中的properties节点
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
//第2步:解析settings节点,获取用户自定的一些配置(解析settings详细配置参考:http://c.biancheng.net/view/4324.html)。
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
//第3步:解析typeAliases节点,获取定义的别名(所谓别名:就是吧你指定的别名对应的class存储在一个Map当中)。
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
//第4步:解析plugins节点,加载用户自定义的插件(插件类需要继承Interceptor接口)。
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
//第5步:解析objectFactory节点,用户可以自定义objectFactory实例化对象的行为。
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
//第6步:解析objectWrapperFactory节点,MyBatis提供在构造对象的时候,用户可自行特殊处理(参考:https://blog.csdn.net/ycxzuoxin/article/details/104843818/)。
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
//第7步:解析reflectorFactory节点,添加用户自定义的对象辅助性工厂类。
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
//第8步:解析environments节点,环境集合属性对象,用于获取数据库的连接信息。
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
//第9步:解析databaseIdProvider节点,用于支持多类型数据库(比如同时需要连接mysql和oracle数据库)。
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
//第10步:解析typeHandlers节点,配置jdbc类型和java类型的转换(通常用mybatis默认的)。
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
//第11步:解析mappers节点,读取Mapper配置文件中的sql配置(读取有3中方式:resource,url,class,详情参考:https://blog.csdn.net/fageweiketang/article/details/80835733)。
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}mapper的解析再org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLConfigBuilder.mapperElement()方法第11步中。
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
//遍历解析mappers节点
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
//解析package节点(package扫描的方式在主配置文件中挂载mapper的文件)
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
//解析mapper
//resource,url,class三个值只能有一个值是有值的。
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//如果没有配置resource,则默认解析resource.xml文件
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}接着看 mapperParser.parse()方法
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
//绑定Namespace里面的Class对象
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
//重新解析之前解析不了的节点
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
//解析mapper文件里面的mapper节点
//拿到里面配置的配置项 最终封装成一个MapperedStatemanet
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
//解析<cache-ref namespace=""/>标签(cache-ref用来来引用另外一个命名空间的缓存,用于共享指定命名空间相同的缓存配置和实例)
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
//解析<cache/>标签,动态设置namespace的相应缓存策略(可参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/wuzhenzhao/p/11103043.html)
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
//解析<parameterMap>,它用于指定实体类字段属性与数据库字段属性的映射关系。
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
//解析<resultMap>,它将查询结果集中的列,一一映射到实体类的各个属性。
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
//解析SQL片段,这里并不会真正的去解析SQL片段,只是把XNode放入一个名字为:sqlFragments的Map当中去。
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
//解析xml中的select|insert|update|delete等标签
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}解析xml中的select|insert|update|delete等标签
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
//解析xml节点
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
//xml语句有问题时 存储到集合中 等解析完能解析的再重新解析
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}具体解析xml节点的代码
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
//是否刷新缓存 默认值:增删改操作刷新 查询操作不刷新
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
//是否使用二级缓存 默认值:查询操作使用 增删改操作不使用
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
//是否需要处理嵌套查询结果 group by
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
//替换Includes标签(SQL片段复用)为对应的sql标签里面的值
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
//解析配置的自定义脚本语言驱动 mybatis plus
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
//解析selectKey(为了解决Insert数据时不支持主键自动生成的问题)
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
//设置主键自增规则
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
//解析Sql
//根据sql文本来判断是否需要动态解析,如果没有动态sql语句且只有#{}的时候直接静态解析使用?占位
//当有${}不解析
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
if (resultSetTypeEnum == null) {
resultSetTypeEnum = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
}
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}五,mybatis如何进行SQL复用
//解析SQL片段,这里并不会真正的去解析SQL片段,只是把XNode放入一个名字为:sqlFragments的Map当中去。
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));下面代码中,如下则是sql复用的解析代码,调用的是XMLIncludeTransformer.applyIncludes();
//替换Includes标签(SQL片段复用)为对应的sql标签里面的值
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
public void applyIncludes(Node source) {
Properties variablesContext = new Properties();
Properties configurationVariables = configuration.getVariables();
Optional.ofNullable(configurationVariables).ifPresent(variablesContext::putAll);
applyIncludes(source, variablesContext, false);
}
/**
* Recursively apply includes through all SQL fragments.
* @param source Include node in DOM tree
* @param variablesContext Current context for static variables with values
*/
private void applyIncludes(Node source, final Properties variablesContext, boolean included) {
if (source.getNodeName().equals("include")) {
//获取refid指向的sql标签(前面提到的sqlFragments这个Map)对象的深拷贝。
Node toInclude = findSqlFragment(getStringAttribute(source, "refid"), variablesContext);
//获取include标签下的property子标签列表(property用于动态传参),与variablesContext合并返回新的Properties对象。
Properties toIncludeContext = getVariablesContext(source, variablesContext);
//递归处理
applyIncludes(toInclude, toIncludeContext, true);
if (toInclude.getOwnerDocument() != source.getOwnerDocument()) {
toInclude = source.getOwnerDocument().importNode(toInclude, true);
}
//替换include标签为sql标签
source.getParentNode().replaceChild(toInclude, source);
while (toInclude.hasChildNodes()) {
//将sql的子标签添加到sql标签的前面
toInclude.getParentNode().insertBefore(toInclude.getFirstChild(), toInclude);
}
//移除sql标签
toInclude.getParentNode().removeChild(toInclude);
} else if (source.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
if (included && !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {
// 解析 ${} 占位符
NamedNodeMap attributes = source.getAttributes();
for (int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) {
Node attr = attributes.item(i);
attr.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(attr.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
}
//遍历处理当前SQL语句标签的子标签
NodeList children = source.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
//递归处理
applyIncludes(children.item(i), variablesContext, included);
}
} else if (included && (source.getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE || source.getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE)
&& !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {
//替换占位符为variablesContext中对应的配置值,这里替换的是引用sql标签中定义的语句片段中对应的占位符。
source.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(source.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
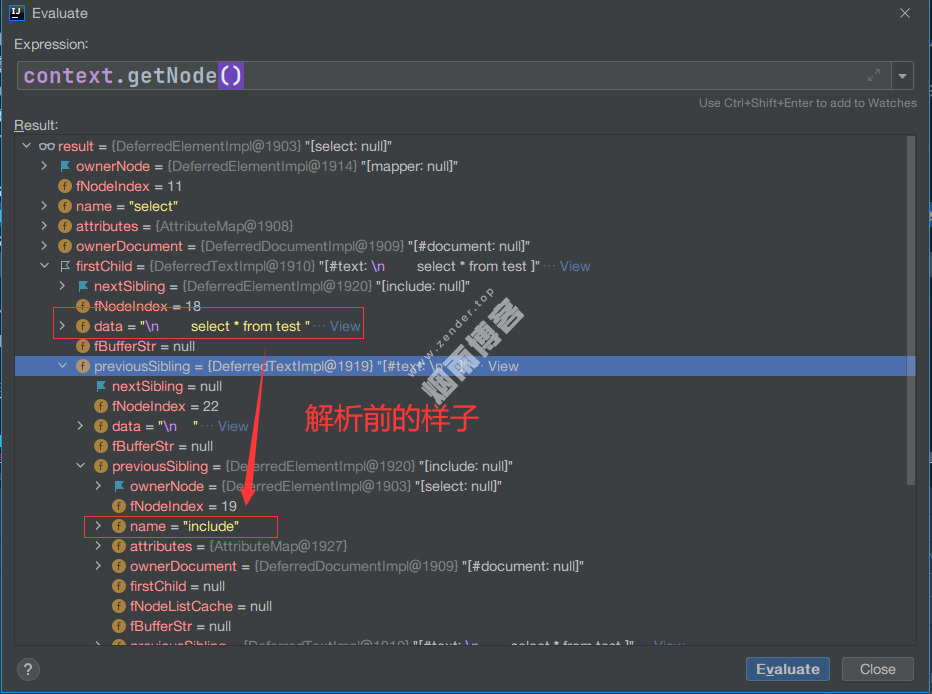
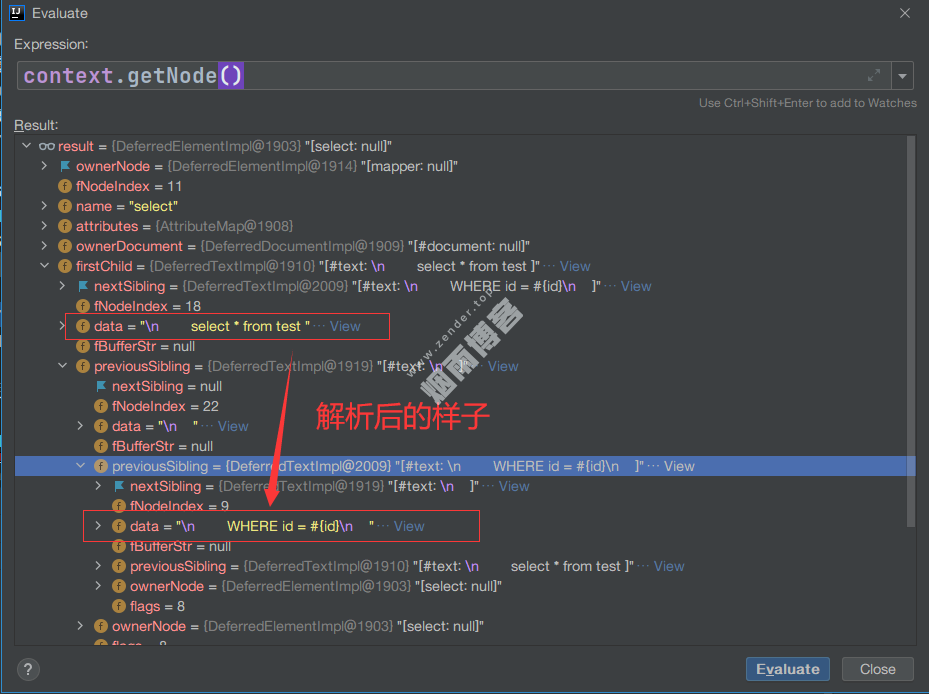
}例如有一个mapper.xml内容如下:
<mapper namespace="com.DemoMapper">
<sql id="test_sql">
WHERE id = #{id}
</sql>
<select id="selectAll" parameterType="Map" resultType="Map">
select * from test <include refid="test_sql"/>
</select>
</mapper>如下截图是解析前后对应Node的变化。
六,动态/静态SQL解析
静态sql解析,条件为:根据sql文本来判断是否需要动态解析,如果没有动态sql语句(if else啥的)且只有#{}的时候直接静态解析使用?占位。当有${}不解析。
//解析Sql
//根据sql文本来判断是否需要动态解析,如果没有动态sql语句且只有#{}的时候直接静态解析使用?占位
//当有${}不解析
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
//XMLLanguageDriver.createSqlSource()
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}
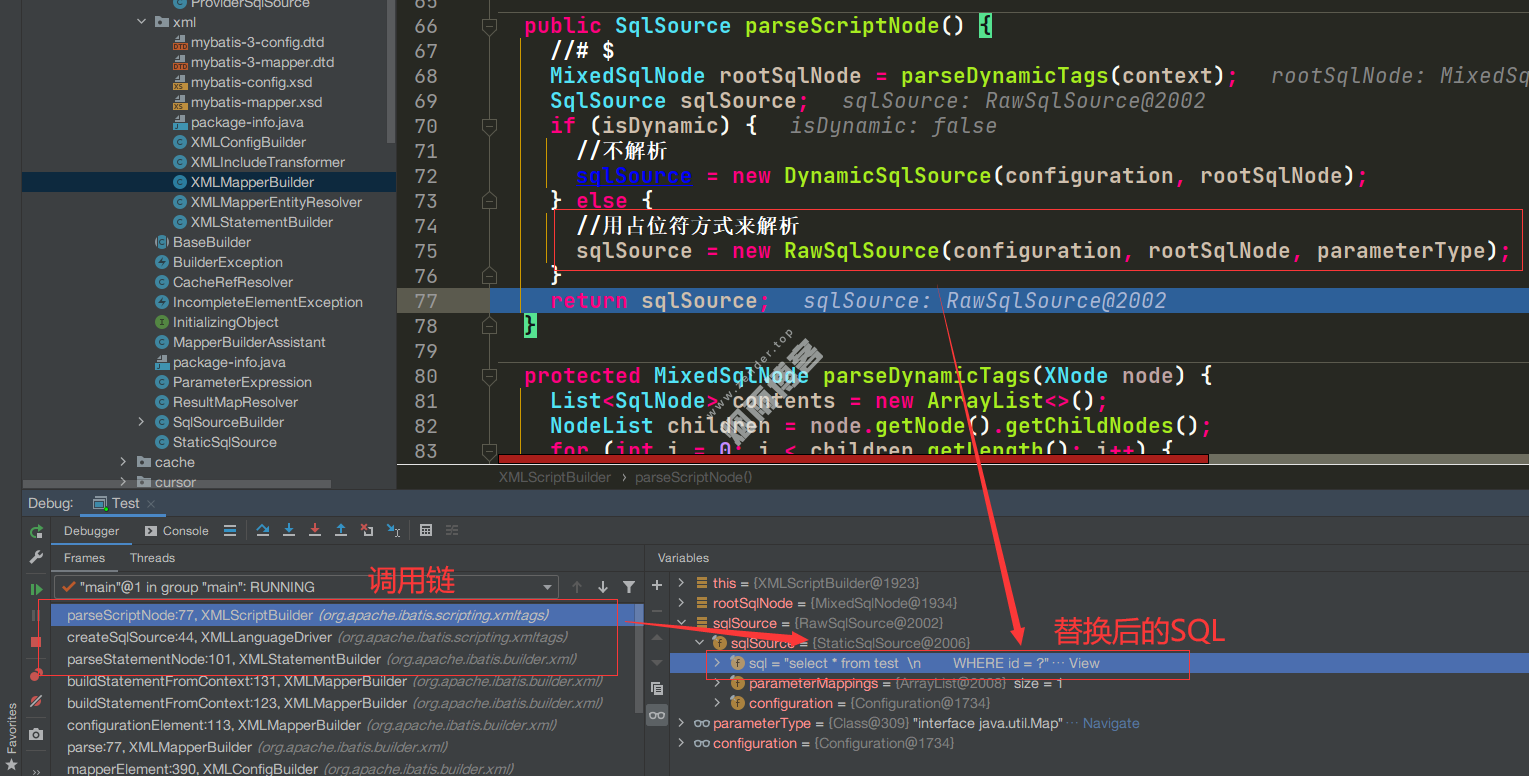
//XMLScriptBuilder.parseScriptNode()
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
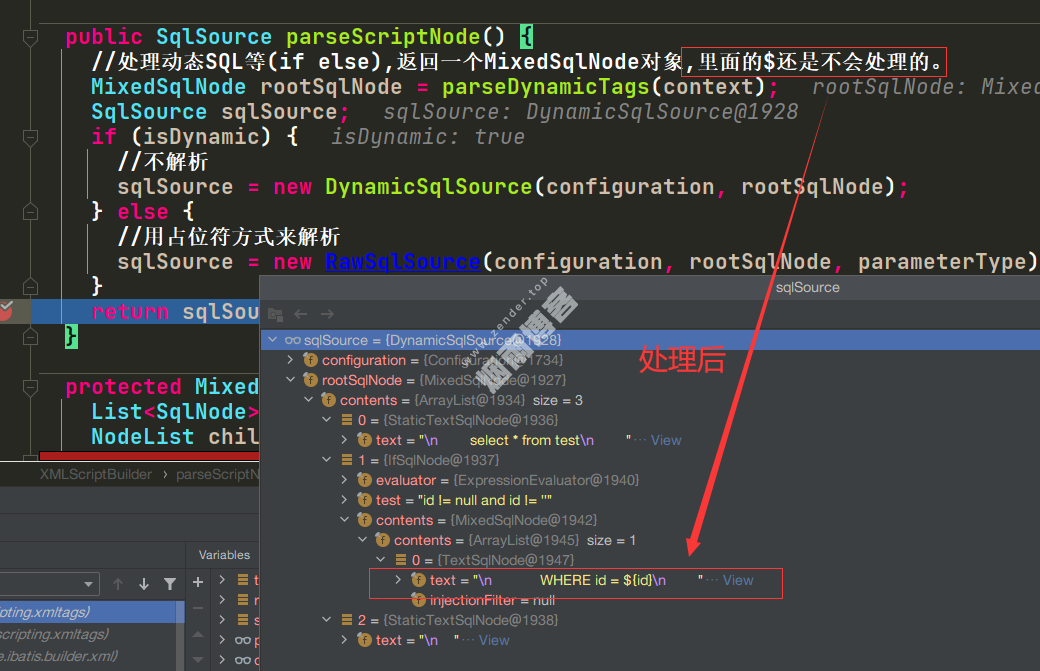
//处理动态SQL等(if else),返回一个MixedSqlNode对象,里面的$还是不会处理的。
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource;
if (isDynamic) {
//不解析
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
//用占位符方式来解析
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
String data = child.getStringBody("");
//当解析的是纯SQL文本(例如:select * from test),直接封装成TextSqlNode
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // issue #628
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
//动态sql时,会根据不同的nodeName,获取不同的NodeHandler来解析。
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
isDynamic = true;
}
}
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}6.1、静态SQL解析
<mapper namespace="com.DemoMapper">
<sql id="test_sql">
WHERE id = #{id}
</sql>
<select id="selectAll" parameterType="Map" resultType="Map">
select * from test <include refid="test_sql"/>
</select>
</mapper>6.2、动态SQL解析
<mapper namespace="com.DemoMapper">
<select id="selectAll" parameterType="Map" resultType="Map">
select * from test
<if test="id != null and id != ''">
WHERE id = ${id}
</if>
</select>
</mapper>6.2.1、这里为什么不解析$
6.3、处理$
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
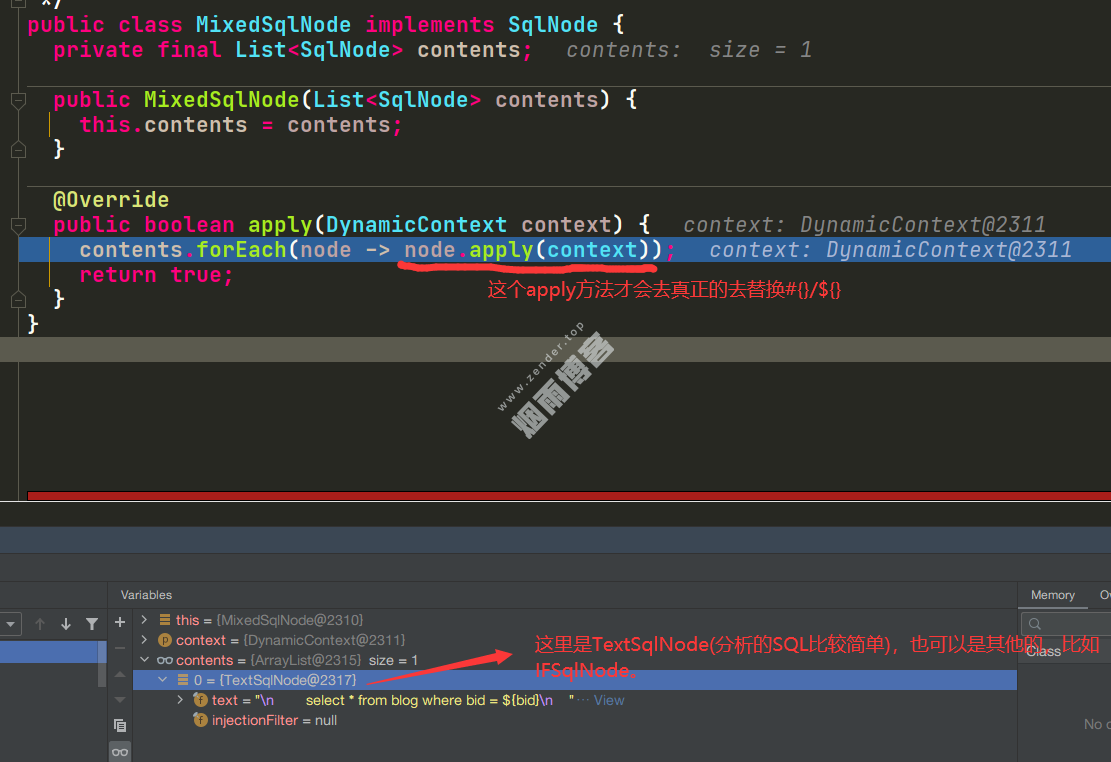
//apply方法就会去处理${}和#{}
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
context.getBindings().forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter);
return boundSql;
}分配给MixedSqlNode类去处理(sql不同,分配的)。
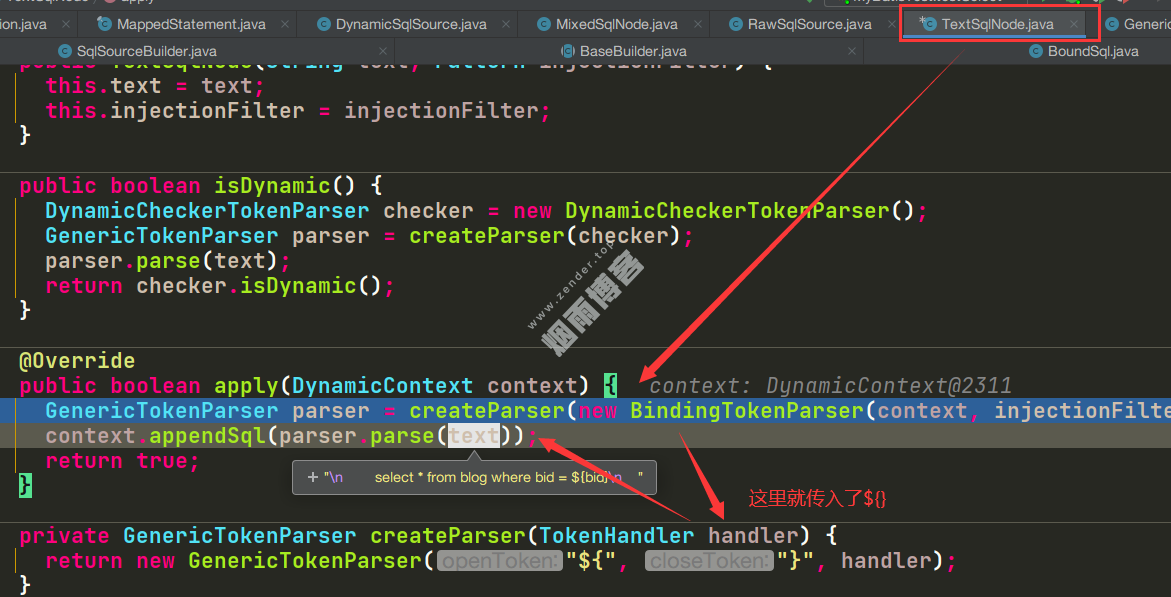
这样就看到使用了GenericTokenParser.parse()方法处理#和$
public class GenericTokenParser {
private final String openToken;
private final String closeToken;
private final TokenHandler handler;
//根据构造函数传入的openToken,closeToken来确认是去处理${}还是#{}
public GenericTokenParser(String openToken, String closeToken, TokenHandler handler) {
this.openToken = openToken;
this.closeToken = closeToken;
this.handler = handler;
}
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
int start = text.indexOf(openToken);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
//遍历里面所有的#{} select ? ,#{id1} ${},并做处理和替换。
while (start > -1) {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
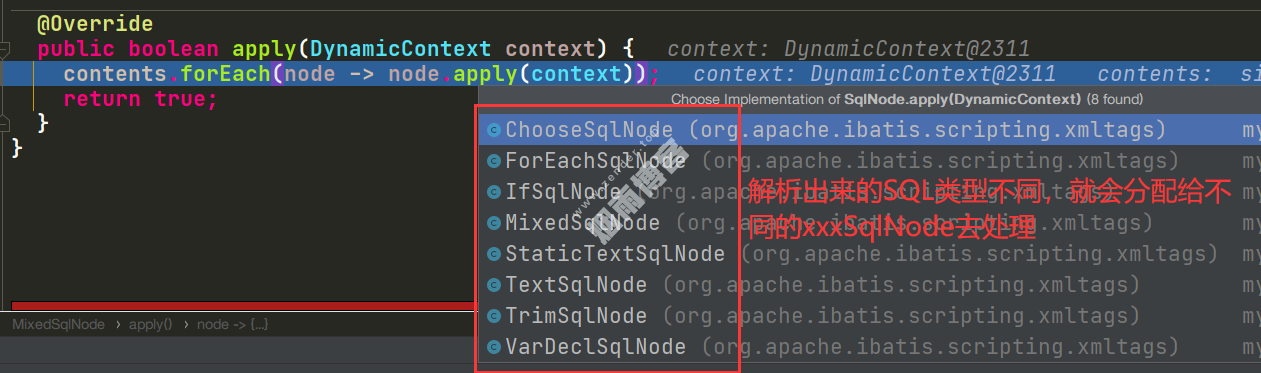
}MyBatis里面有8中不同xxxSqlNode。每种SqlNode的parse()方法来处理相应的动态SQL,截图如下:
版权声明
非特殊说明,本文由Zender原创或收集发布,欢迎转载。
 ZENDER
ZENDER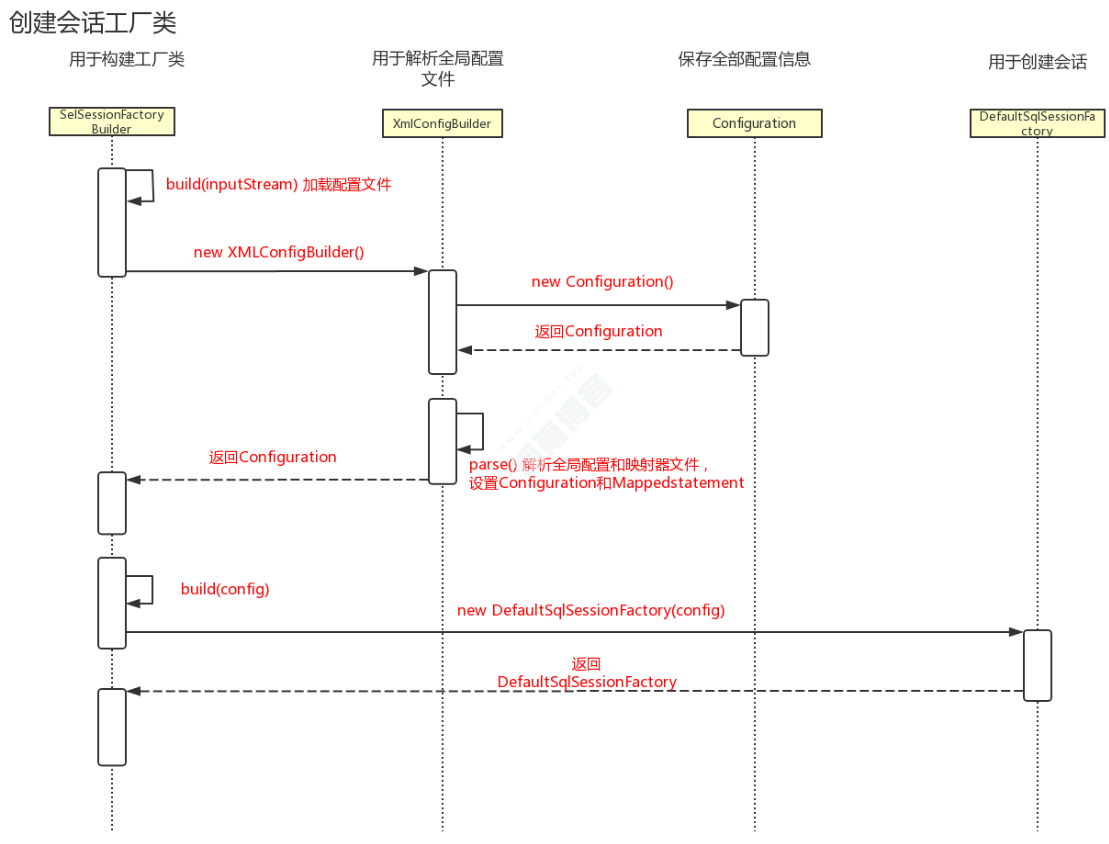


发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。