6、Spring源码-依赖注入(下)
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
//resolveDependency方法定义
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
}该方法传入一个依赖描述(DependencyDescriptor)descriptor,该方法会根据该依赖描述从BeanFactory中找出对应的唯一的一个Bean对象,然后返回。
比如注入的是字段类型的,从AutowiredFieldElement#inject()开始。
//对字段进行注入
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
//获取注入元素对象
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
//如果当前对象在容器中被缓存
if (this.cached) {
//根据Bean名称解析缓存中的字段值
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
//如果当前对象没有被容器缓存
else {
//创建一个字段依赖描述符
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
//获取容器中的类型转换器
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
//根据容器中Bean定义,解析指定的依赖关系,获取依赖对象
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
//线程同步,确保容器中数据一致性
synchronized (this) {
//如果当前对象没有被容器缓存
if (!this.cached) {
//获取到了当前对象的依赖对象,并且required属性为true
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
//为指定Bean注册依赖Bean
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
//如果容器中有指定名称的Bean对象
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName)) {
//依赖对象类型和字段类型匹配,默认按类型注入
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
//创建一个依赖对象的引用,同时缓存
this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
}
//如果获取的依赖关系为null,且获取required属性为false
else {
//将字段值的缓存设置为null
this.cachedFieldValue = null;
}
//容器已经对当前字段的值缓存
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
//如果字段依赖值不为null
if (value != null) {
//显式使用JDK的反射机制,设置自动的访问控制权限为允许访问
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
//为Bean对象的字段设置值
field.set(bean, value);
}
}第一次解析是没有缓存的,会进入resolvedCachedArgument()方法。
@Nullable
private Object resolvedCachedArgument(@Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object cachedArgument) {
// 判断是否是一个依赖描述器
if (cachedArgument instanceof DependencyDescriptor) {
DependencyDescriptor descriptor = (DependencyDescriptor) cachedArgument;
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
return this.beanFactory.resolveDependency(descriptor, beanName, null, null);
}
else {
return cachedArgument;
}
}DefaultListableBeanFactory.resolveDependency()方法
@Override
@Nullable
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
//用来获取参数名字
descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(getParameterNameDiscoverer());
//判断是否进行Optional包装处理
if (Optional.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return createOptionalDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
//判断是否进行ObjectFactory或ObjectProvider的延迟加载的处理
else if (ObjectFactory.class == descriptor.getDependencyType() ||
ObjectProvider.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return new DependencyObjectProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
//Jsr330规范相关处理
else if (javaxInjectProviderClass == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
return new Jsr330ProviderFactory().createDependencyProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
else {
//理依赖注入逻辑
//在属性/set方法上使用了@Lazy注解,那么构造一个代理对象进行返回,真正使用代理对象的时候才进行Bean筛选
//ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver.getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary()方法会调用
//isLazy()和buildLazyResolutionProxy()
//其中buildLazyResolutionProxy()会调用到doResolveDependency()获取注入的Bean
Object result = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(
descriptor, requestingBeanName);
//如果没有代理对象
if (result == null) {
//descriptor表示某个方法的参数/set方法
//requestingBeanName表示正在进行依赖注入的BeanName
result = doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
return result;
}
}doResolveDependency()方法
@Nullable
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
//如果当前descriptor之前做过依赖注入,直接取出返回。相当于一个缓存
Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
if (shortcut != null) {
return shortcut;
}
//获取类型,有可能是字段类型,有可能是方法类型
Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
//处理@Value,获取@Value的值
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof String) {
//占位符填充(${})
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ? getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
//解析Spring表达式(#{})
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
//将value转化为descriptor所对应的类型
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}
//如果descriptor所对应的是:数组/List/Map这些。就将descriptor对应的类型所匹配的Bean放入multipleBeans,返回。
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
if (multipleBeans != null) {
return multipleBeans;
}
//找到所有Bean,key是BeanName,value有可能是Bean对象,也有可能是beanClass
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;
}
String autowiredBeanName;
Object instanceCandidate;
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
//根据类型找到多个,做进一步的筛选,@Primary --> 优先级(数字越小的优先级越高) --> name
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(type, matchingBeans);
}
else {
// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:
// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans
// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).
return null;
}
}
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}
else {
// We have exactly one match.
Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();
autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey();
instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();
}
//记录匹配过的BeanName
if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {
autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);
}
//有可能筛选出来的是某个Bean的类型,此处就进行实例化,调用getBean
if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {
instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);
}
Object result = instanceCandidate;
if (result instanceof NullBean) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
result = null;
}
if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, result)) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(autowiredBeanName, type, instanceCandidate.getClass());
}
return result;
}
finally {
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
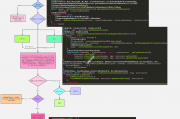
}以上大致是DefaultListableBeanFactory中resolveDependency()方法的实现,具体流程图如图:
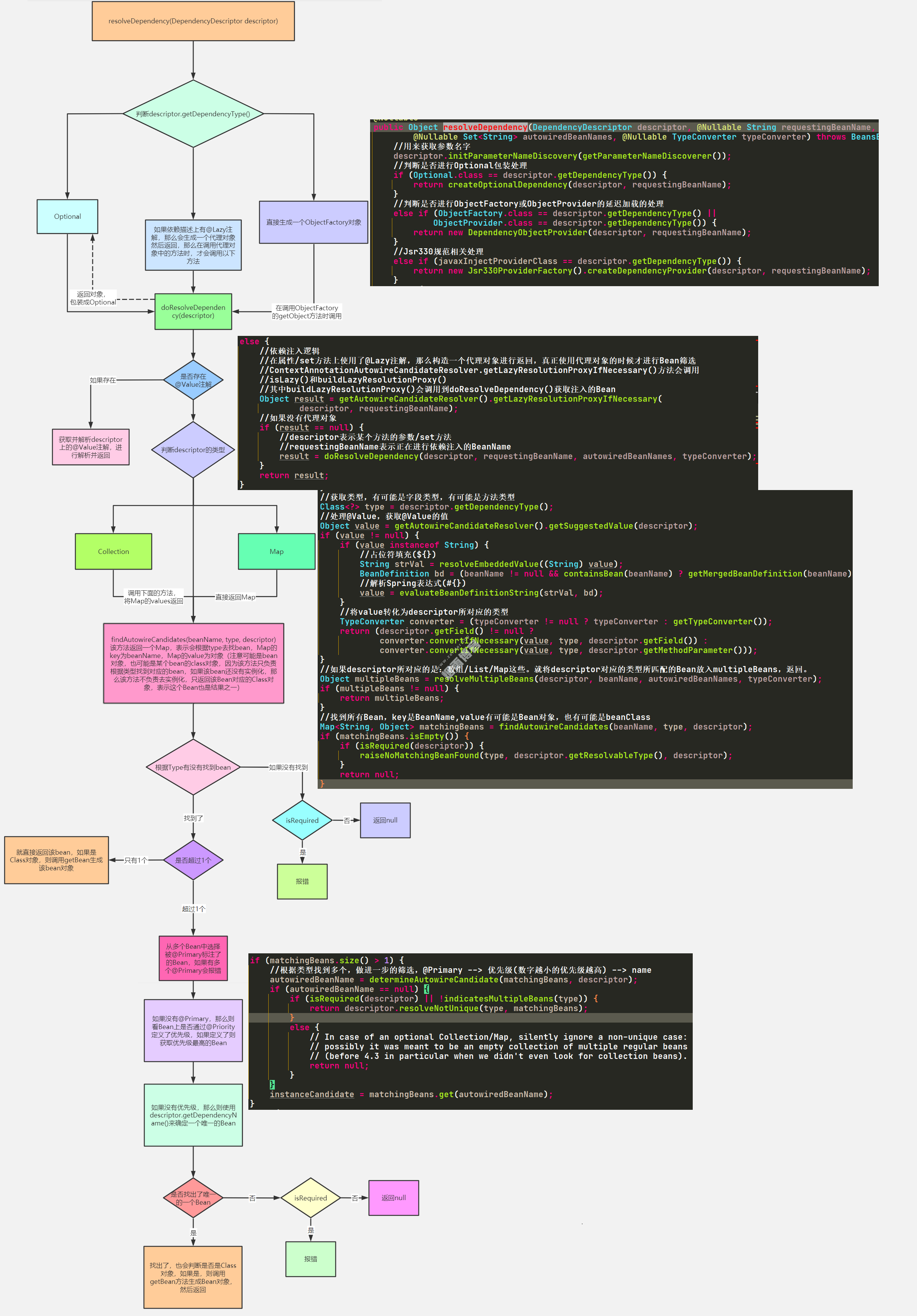 接下来看Spring是如何寻找Bean的,关键代码在doResolveDependency()中的findAutowireCandidates()方法中,基于一个类型type找Bean。
接下来看Spring是如何寻找Bean的,关键代码在doResolveDependency()中的findAutowireCandidates()方法中,基于一个类型type找Bean。
//找到所有Bean,key是BeanName,value有可能是Bean对象,也有可能是beanClass Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
如何去找所匹配的BeanNames
protected Map<String, Object> findAutowireCandidates(
@Nullable String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
//从BeanFactory中找出和requiredType所匹配的beanName
//这些beanName所对应的Bean不一定经过实例化过程
//只有到最终确定某个Bean了,如果这个Bean还没有实例化才会真正进行实例化
String[] candidateNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this, requiredType, true, descriptor.isEager());
Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<>(candidateNames.length);
//根据类型resolvableDependencies中匹配的bean
//resolvableDependencies中存放的是类型:Bean对象
//比如BeanFactory.class:BeanFactory对象,在Spring启动时会对resolvableDependencies这个缓存放入数据,存储的是一个类型所对应的Bean对象
for (Class<?> autowiringType : this.resolvableDependencies.keySet()) {
if (autowiringType.isAssignableFrom(requiredType)) {
Object autowiringValue = this.resolvableDependencies.get(autowiringType);
autowiringValue = AutowireUtils.resolveAutowiringValue(autowiringValue, requiredType);
if (requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) {
result.put(ObjectUtils.identityToString(autowiringValue), autowiringValue);
break;
}
}
}
//这里如果匹配到了2个bean,其中一个是自己,不会先注入自己,优先注入非自己的那个bean
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
//如果不是自己,则判断该candidate到底能不能用来进行自动注入
//isAutowireCandidate()判断是否可以依赖注入,处理的是注解@Bean的参数autowireCandidate,默认值为true
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, descriptor)) {
//向result放入所匹配的候选Bean
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
//如果为空,要么是真的没有注入的,要么是注入的自己
if (result.isEmpty() && !indicatesMultipleBeans(requiredType)) {
// Consider fallback matches if the first pass failed to find anything...
DependencyDescriptor fallbackDescriptor = descriptor.forFallbackMatch();
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
//isAutowireCandidate()判断是否可以依赖注入,处理的是注解@Bean的参数autowireCandidate,默认值为true
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, fallbackDescriptor)) {
//向result放入所匹配的候选Bean
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
//匹配的是自己,把自己添加到result中,并返回
if (result.isEmpty()) {
// Consider self references as a final pass...
// but in the case of a dependency collection, not the very same bean itself.
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
if (isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) &&
(!(descriptor instanceof MultiElementDescriptor) || !beanName.equals(candidate)) &&
isAutowireCandidate(candidate, fallbackDescriptor)) {
//向result放入所匹配的候选Bean
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}public static String[] beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
ListableBeanFactory lbf, Class<?> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) {
Assert.notNull(lbf, "ListableBeanFactory must not be null");
//从本地容器中找
String[] result = lbf.getBeanNamesForType(type, includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit);
//再从父容器找并放入result
if (lbf instanceof HierarchicalBeanFactory) {
HierarchicalBeanFactory hbf = (HierarchicalBeanFactory) lbf;
if (hbf.getParentBeanFactory() instanceof ListableBeanFactory) {
String[] parentResult = beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
(ListableBeanFactory) hbf.getParentBeanFactory(), type, includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit);
List<String> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
resultList.addAll(Arrays.asList(result));
for (String beanName : parentResult) {
if (!resultList.contains(beanName) && !hbf.containsLocalBean(beanName)) {
resultList.add(beanName);
}
}
result = StringUtils.toStringArray(resultList);
}
}
return result;
}通getBeanNamesForType()方法,具体使用的实现类为DefaultListableBeanFactory,根据一个type寻找匹配的BeanName。
@Override
public String[] getBeanNamesForType(@Nullable Class<?> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) {
//如果没有冻结,就根据类型去BeanFactory找,如果冻结了,可能就跳过这个if然后去缓存中去拿了
if (!isConfigurationFrozen() || type == null || !allowEagerInit) {
return doGetBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType.forRawClass(type), includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit);
}
//把当前类型所匹配的beanName缓存起来
//includeNonSingletons参数的意思,获取时是否包不包括非单例Bean.
//true:查询所有bean缓存(allBeanNamesByType) false:只查询单例Bean缓存(singletonBeanNamesByType)
Map<Class<?>, String[]> cache =
(includeNonSingletons ? this.allBeanNamesByType : this.singletonBeanNamesByType);
String[] resolvedBeanNames = cache.get(type);
if (resolvedBeanNames != null) {
return resolvedBeanNames;
}
//缓存如果为命中
resolvedBeanNames = doGetBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType.forRawClass(type), includeNonSingletons, true);
if (ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(type, getBeanClassLoader())) {
cache.put(type, resolvedBeanNames);
}
return resolvedBeanNames;
}调用另一个重载方法doGetBeanNamesForType()
private String[] doGetBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
// Check all bean definitions.
//遍历所有的BeanDefinitions
for (String beanName : this.beanDefinitionNames) {
// Only consider bean as eligible if the bean name
// is not defined as alias for some other bean.
if (!isAlias(beanName)) {
try {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// Only check bean definition if it is complete.
//判断mbd允不允许获取对应类型
//首先mdb不能是抽象的,然后allowEagerInit为true,则直接去推测mdb的类型,并进行匹配
//如果allowEagerInit为false,那就继续判断,如果mdb还没有加载类并且是懒加载的并且不允许提前加载类,那mbd不能用来进行匹配(因为不允许提前加载类,只能在此mdb自己去创建bean对象时才能去创建类)
//如果allowEagerInit为false,并且mbd已经加载类了,或者是非懒加载的,或者允许提前加载类,并且不用必须提前初始化才能获取类型,那么就可以去进行匹配了
//这个条件有点复杂,但是如果只考虑大部分流程,则可以忽略这个判断,因为allowEagerInit传进来的基本上都是true
if (!mbd.isAbstract() && (allowEagerInit ||
((mbd.hasBeanClass() || !mbd.isLazyInit() || isAllowEagerClassLoading())) &&
!requiresEagerInitForType(mbd.getFactoryBeanName()))) {
// In case of FactoryBean, match object created by FactoryBean.
//是否是一个FactoryBean
boolean isFactoryBean = isFactoryBean(beanName, mbd);
BeanDefinitionHolder dbd = mbd.getDecoratedDefinition();
//在筛选Bean时,如果仅仅只包括单例,但是beanName对应的又不是单例,则忽略
boolean matchFound =
(allowEagerInit || !isFactoryBean ||
(dbd != null && !mbd.isLazyInit()) || containsSingleton(beanName)) &&
(includeNonSingletons ||
(dbd != null ? mbd.isSingleton() : isSingleton(beanName))) &&
isTypeMatch(beanName, type);
//当前BeanDefinition不是FactoryBean,也就是普通Bean
if (!matchFound && isFactoryBean) {
// In case of FactoryBean, try to match FactoryBean instance itself next.
beanName = FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName;
matchFound = (includeNonSingletons || mbd.isSingleton()) && isTypeMatch(beanName, type);
}
if (matchFound) {
result.add(beanName);
}
}
}
catch (CannotLoadBeanClassException ex) {
if (allowEagerInit) {
throw ex;
}
// Probably contains a placeholder: let's ignore it for type matching purposes.
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Ignoring bean class loading failure for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
onSuppressedException(ex);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
if (allowEagerInit) {
throw ex;
}
// Probably contains a placeholder: let's ignore it for type matching purposes.
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Ignoring unresolvable metadata in bean definition '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
onSuppressedException(ex);
}
}
}接下来看isAutowireCandidate()方法
@Override
public boolean isAutowireCandidate(String beanName, DependencyDescriptor descriptor)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
return isAutowireCandidate(beanName, descriptor, getAutowireCandidateResolver());
}流程如下
1、先判断beanName对应的BeanDefinition中的autowireCandidate属性,如果为false,表示不能用来进行自动注入,如果为true则继续进行判断。SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver#isAutowireCandidate()
default boolean isAutowireCandidate(BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
return bdHolder.getBeanDefinition().isAutowireCandidate();
}2、判断当前type是不是泛型,如果是泛型是会把容器中所有的beanName找出来的,如果是这种情况,那么在这一步中就要获取到泛型的真正类型,然后进行匹配,如果当前beanName和当前泛型对应的真实类型匹配,那么则继续判断。GenericTypeAwareAutowireCandidateResolver#isAutowireCandidate()
@Override
public boolean isAutowireCandidate(BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
if (!super.isAutowireCandidate(bdHolder, descriptor)) {
// If explicitly false, do not proceed with any other checks...
return false;
}
return checkGenericTypeMatch(bdHolder, descriptor);
}3、如果当前DependencyDescriptor上存在@Qualifier注解,那么则要判断当前beanName上是否定义了Qualifier,并且是否和当前DependencyDescriptor上的Qualifier相等,相等则匹配。QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver#isAutowireCandidate()
@Override
public boolean isAutowireCandidate(BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
// 先执行上层判断匹配(第二步的泛型匹配),如果匹配成功,在自己匹配
boolean match = super.isAutowireCandidate(bdHolder, descriptor);
if (match) {
// descriptor.getAnnotations()拿得是属性或方法参数前的注解,拿不到方法上的注解
match = checkQualifiers(bdHolder, descriptor.getAnnotations());
if (match) {
MethodParameter methodParam = descriptor.getMethodParameter();
if (methodParam != null) {
Method method = methodParam.getMethod();
if (method == null || void.class == method.getReturnType()) {
// methodParam.getMethodAnnotations()实际上拿得的是方法上的注解
match = checkQualifiers(bdHolder, methodParam.getMethodAnnotations());
}
}
}
}
return match;
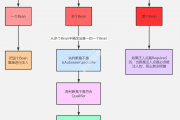
}大致流程图
版权声明
非特殊说明,本文由Zender原创或收集发布,欢迎转载。
 ZENDER
ZENDER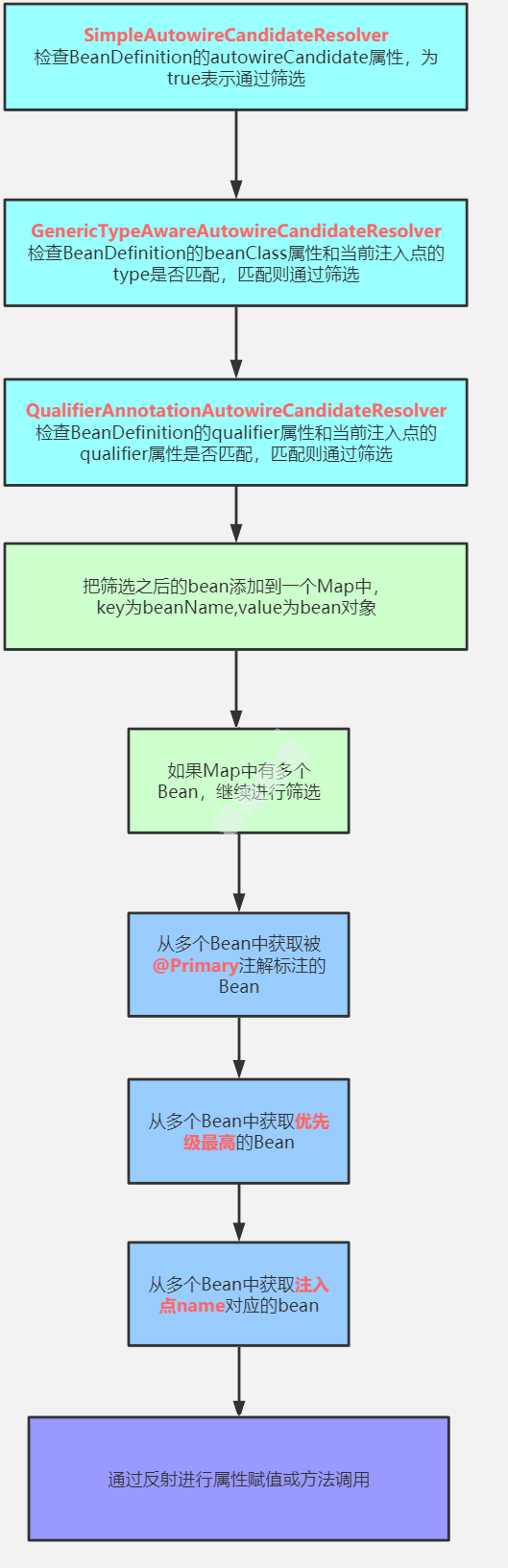

发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。