2、常用到的注解列表-生命周期相关
1、@Bean
使用@Bean注解中的initMethod(初始化)、destroyMethod(销毁)来指定指定初始化方法和销毁方法。
/**
* bean的生命周期:bean的创建->初始化->销毁的过程
* 容器管理bean的生命周期:
* 我们可以自定义初始化方法和销毁的方法:容器在bean进行到当前的生命周期的时候,来调用我们自定义的初始化方法和销毁方法
* 构造(对象创建):
* 单实例:在容器启动的时候创建对象
* 多实例:在每次获取的时候来创建对象
* 初始化方法:
* 对象创建完成,并赋值好,调用初始化方法。
* 销毁方法:
* 单实例的bean:在容器关闭的时候进行销毁。
* 多实例的bean:容器不会管理这个bean,容器不会调用销毁的方法。
*
* 1)指定初始化方法和销毁方法;
* -我们可以通过@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")来指定初始化方法和销毁方法
* 相当于xml配置文件bean标签里面的 init-method="" 和 destroy-method="" 属性
*/
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfLifeCycle {
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Car car() {
return new Car();
}
}当bean的作用域为多例的时候,只有在获取的时候,才会创建对象,而且在IOC容器关闭的时候,是不进行销毁的。
通过bean实现InitializingBean接口、DisposableBean接口来管理生命周期。
public interface InitializingBean {
/**
* 在bean的构造方法调用之后进行调用。
*/
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}public interface DisposableBean {
/**
* 在bean被销毁后调用。
*/
void destroy() throws Exception;
}例如
@Component
public class Cat implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public Cat() {
System.out.println("Cat...Contrustor...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Cat...afterPropertiesSet...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Cat...destroy...");
}
}2、@PostConstruct&@PreDestroy
可以使用JSR250规范里面定义的两个注解
@PostConstruct :在bean创建完成并且属性赋值完成,来执行初始化方法。
@PreDestroy :在容器销毁bean之前通知我们来进行清理工作。
@Component
public class Dog {
public Dog() {
System.out.println("Dog...Contructor...");
}
//在对象创建并赋值之后(构造方法调用完成后)调用。
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("Dog...@PostConstruct...");
}
//在对象销毁之后调用。
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("Dog...@PreDestroy...");
}
}3、BeanPostProcessor-后置处理器
BeanPostProcessor接口:bean的后置处理器,在bean初始化前后做一些处理工作,这个接口有两个方法:
postProcessBeforeInitialization():在初始化之前(构造方法调用前)工作。
postProcessAfterInitialization():在初始化之后(构造方法调用后)工作。
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//方法里面可以通过bean、beanName来确定那些bean是需要我们提前做一些处理工作的。
System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization..."+beanName+"=>"+bean);
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization..."+beanName+"=>"+bean);
return bean;
}
}Spring底层中很多地方都是BeanPostProcessor来完成的。
bean赋值,注入其他组件,@Autowired、生命周期注解等功能、@Async等等都是使用BeanPostProcessor来完成的。
4、ApplicationContextAware-获取IOC容器对象applicationContext
如果我们想要获取IOC容器,我们可以这样做:
@Component
public class Dog implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public Dog() {
System.out.println("Dog...Contructor...");
}
//在对象创建并赋值之后调用
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("Dog...@PostConstruct...");
}
//在对象创建并赋值之后调用
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("Dog...@PreDestroy...");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}版权声明
非特殊说明,本文由Zender原创或收集发布,欢迎转载。
上一篇:1、常用到的注解列表-bean相关 下一篇:3、常用到的注解列表-属性赋值相关
 ZENDER
ZENDER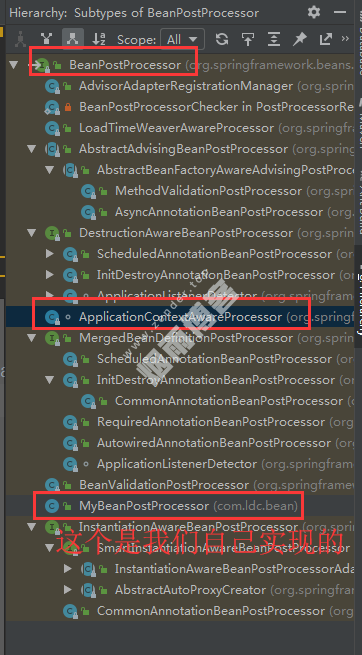


发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。