1、Spring中的基本概念-BeanDefinition(Bean的定义)
1、Bean
被Spring管理的对象叫做Bean。
2、BeanDefinition(Bean定义)
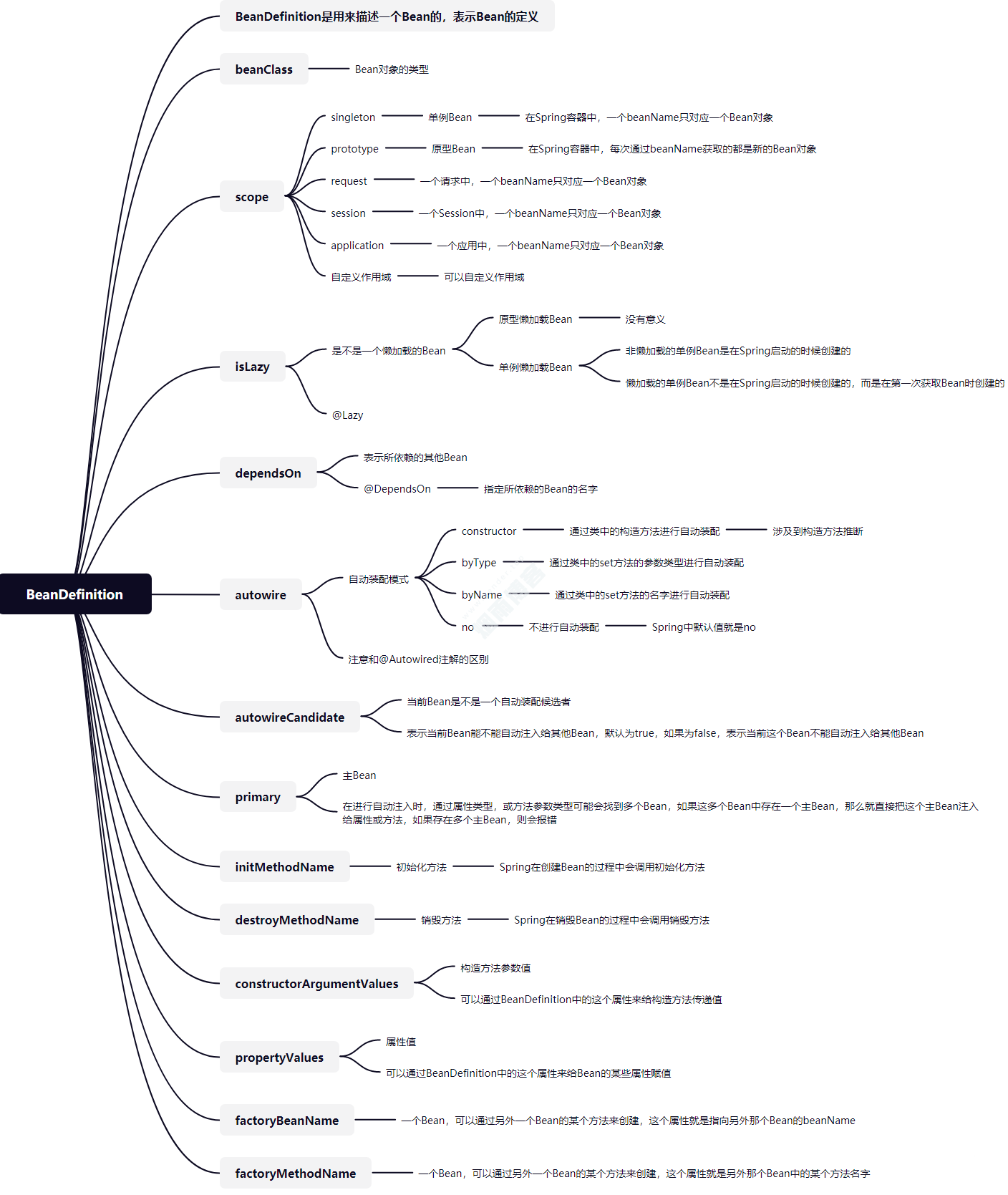
BeanDefinition是用来描述一个Bean的,表示Bean的定义。
BeanDefinition是一个接口,定义了一系列Bean所需要的东西。接口定义如下:
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement {
/**
* 单例bean,在Spring容器中,一个beanName只对应一个Bean对象。
* Scope:singleton
*/
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON;
/**
* 原型bean,在Spring容器中,每次通过beanName获取的都是新的Bean对象。
* Scope:prototype
*/
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a major part
* of the application. Typically corresponds to a user-defined bean.
*/
int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a supporting
* part of some larger configuration, typically an outer
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
* {@code SUPPORT} beans are considered important enough to be aware
* of when looking more closely at a particular
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition},
* but not when looking at the overall configuration of an application.
*/
int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is providing an
* entirely background role and has no relevance to the end-user. This hint is
* used when registering beans that are completely part of the internal workings
* of a {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
*/
int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2;
/**
* 设置此bean定义的父定义的名称(如果有)
*/
void setParentName(@Nullable String parentName);
/**
* 获取此bean定义的父定义的名称(如果有)
*/
@Nullable
String getParentName();
/**
* 指定此bean定义的bean类名。
* 在bean factory后期处理过程中可以修改类名,
*/
void setBeanClassName(@Nullable String beanClassName);
/**
* 获取此bean定义的bean类名
*/
@Nullable
String getBeanClassName();
/**
* 设置bean的目标作用域
*/
void setScope(@Nullable String scope);
/**
* 获取bean的目标作用域
*/
@Nullable
String getScope();
/**
* 设置是否懒加载
*/
void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit);
/**
* 获取是否懒加载
*/
boolean isLazyInit();
/**
* 设置此bean依赖于初始化的bean的名称。
* bean工厂将保证首先初始化这些bean。
*/
void setDependsOn(@Nullable String... dependsOn);
/**
* 返回此bean所依赖的bean名称数组
*/
@Nullable
String[] getDependsOn();
/**
* 设置当前Bean是不是一个自动装配候选者。默认为true,如果为false,表示当前这个Bean不能自动注入给其他Bean。
*/
void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate);
/**
* 获取当前bean是不是一个自动装配候选者。
*/
boolean isAutowireCandidate();
/**
* 设置当前bean是否是一个主bean.
* 在进行自动注入时,通过属性类型,或方法参数类型可能会找到多个Bean,如果这多个Bean中存在一个主Bean,那么就直接把这个主Bean注入给属性或方法,如果存在多个主Bean,则会报错
*/
void setPrimary(boolean primary);
/**
* 获取当前bean是否是一个主bean.
*/
boolean isPrimary();
/**
* 一个Bean,可以通过另外一个Bean的某个方法来创建,这个属性就是指向另外那个Bean的beanName
*/
void setFactoryBeanName(@Nullable String factoryBeanName);
/**
* 获取工厂beanName
*/
@Nullable
String getFactoryBeanName();
/**
* 一个Bean,可以通过另外一个Bean的某个方法来创建,这个属性就是另外那个Bean中的某个方法名字
*/
void setFactoryMethodName(@Nullable String factoryMethodName);
/**
* 获取工厂方法名称
*/
@Nullable
String getFactoryMethodName();
/**
* 构造方法参数值属性,可以通过这个属性来给构造方法传递值
*/
ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues();
/**
* 判断当前bean构造方法是否有参数值
* @since 5.0.2
*/
default boolean hasConstructorArgumentValues() {
return !getConstructorArgumentValues().isEmpty();
}
/**
* 属性值属性,可以通过这个属性来给Bean的某些属性赋值
*/
MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues();
/**
* 判断当前bean是否有属性值
* @since 5.0.2
*/
default boolean hasPropertyValues() {
return !getPropertyValues().isEmpty();
}
/**
* 设置当前bean的初始化方法名称
* @since 5.1
*/
void setInitMethodName(@Nullable String initMethodName);
/**
* 获取设置当前bean的初始化方法名称
* @since 5.1
*/
@Nullable
String getInitMethodName();
/**
* 设置当前bean的销毁方法名称
* @since 5.1
*/
void setDestroyMethodName(@Nullable String destroyMethodName);
/**
* 获取当前bean的销毁方法名称
* @since 5.1
*/
@Nullable
String getDestroyMethodName();
/**
* 设置bean的分类
*/
void setRole(int role);
/**
* 获取bean的分类
*/
int getRole();
/**
* 设置当前bean的描述
* @since 5.1
*/
void setDescription(@Nullable String description);
/**
* 返回当前bean的描述
*/
@Nullable
String getDescription();
/**
* 返回此bean定义的可解决的数据类型,可以通过这个属性来给Bean的某些属性赋值。
* ResolvableType为所有的java类型提供了统一的数据结构以及API,换句话说,一个ResolvableType对象就对应着一种java类型。
* 我们可以通过ResolvableType对象获取类型携带的信息(举例如下):
* getSuperType():获取直接父类型
* getInterfaces():获取接口类型
* getGeneric(int...):获取类型携带的泛型类型
* resolve():Type对象到Class对象的转换
*/
ResolvableType getResolvableType();
/**
* 返回是否是一个单一的、共享的实例
* returned on all calls.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
*/
boolean isSingleton();
/**
* 返回是否使用独立实例
* returned for each call.
* @since 3.0
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
boolean isPrototype();
/**
* 返回这个bean是否是“抽象的”,也就是说,不是要实例化的。
*/
boolean isAbstract();
/**
* 返回此bean定义所定义的资源的描述
*/
@Nullable
String getResourceDescription();
/**
* 返回原始BeanDefinition,如果没有,则返回{@code null}。
*/
@Nullable
BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
}该接口的实现类:
版权声明
非特殊说明,本文由Zender原创或收集发布,欢迎转载。
 ZENDER
ZENDER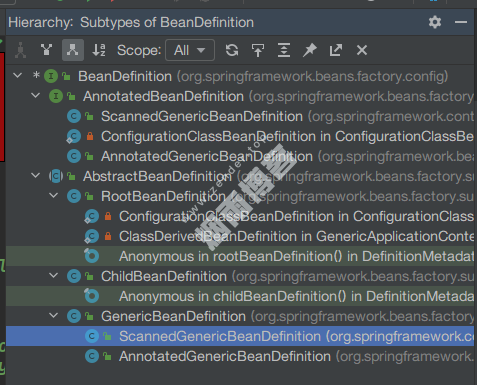


发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。